Applications of Diodes
Uses and Applications of Diodes
A diode is a semiconductor component made of a combination of two layers on P-Type and N-Type material. it is extensively used in electronic devices and other electrical systems. There are a wide range of applications of diodes explained below.
Related Articles:
- What is Diode? Construction & Working of PN Junction Diode
- Types of Diodes and Their Applications – 24 Types of Diodes
Major Applications of Diodes
Following are the various uses and applications of diodes in electrical and electronic systems as follow.
Rectification
Rectification is a method of converting the AC alternating current into the unidirectional DC direct current. The diode is used for the rectification in power supplies to convert the AC supplies from the mains into DC to power any electronic equipment.
The rectification can also be classified into half-wave and full-wave rectification.
Half Wave Rectification
When only one half of the AC cycle i.e. positive half cycle or negative half cycle is rectified or converted into DC, the rectification is called half-wave rectification. Such rectifiers only use one diode and have very low efficiency and power ratings.
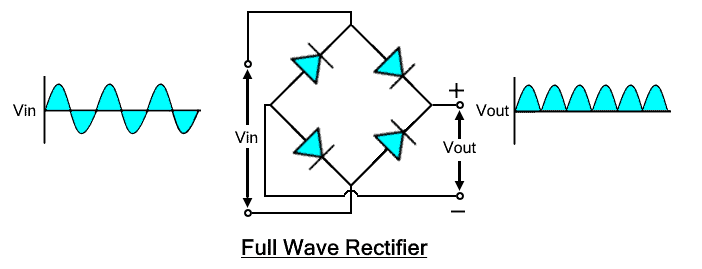
 Full Wave Rectification
Full Wave Rectification
When the full-wave both positive and negative half cycles of the alternating current is converted into DC is called full-wave rectification.
Related Articles:
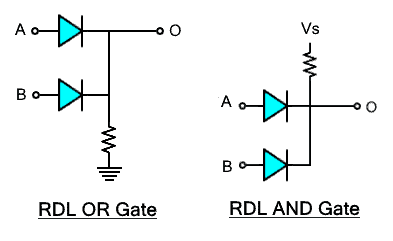
Switching
A diode is basically a switch that turns ON (conduct) in forward bias and turns OFF (do not conduct) in reverse bias. In other words, it allows current in only one direction and blocks it in other direction.
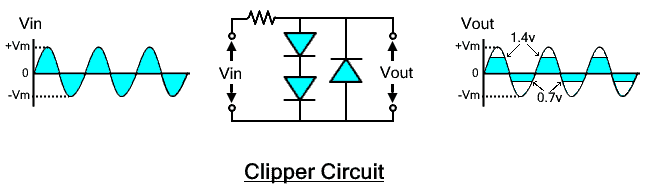
Clipper
Clipper is a circuit mainly consisting of diodes. It is used for shaping an AC signal or waveform. It is used for clipping or cutting a portion from either positive or negative or both halves of the waveform above or below a threshold level.
It changes the shape of the signal. The peak to peak value of the output waveform changes however, there is no DC offset.
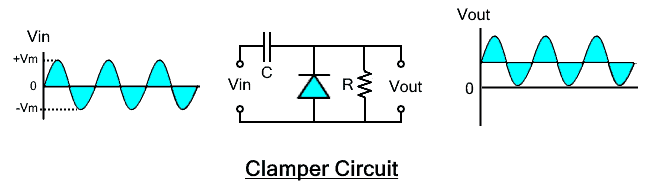
Clamper
A clamper is a circuit that adds in a positive or negative DC shift to the signal. The output signal waveform is not distorted and the peak to peak value remains the same. Only the waveform is lifted above or below the reference line.
Related Articles:
- Shockley Diode: Construction, Working, Characteristics and Applications
- Schottky Diode: Construction, Working, Advantages, & Applications
Voltage Multiplier
A voltage multiplier as its name suggests multiplies the input voltage by a factor determined by the circuit. The circuit is purely made of diode with capacitors.

Source Isolation
Source isolation means that there is no electrical contact between the power source and the load. An optocoupler or opto-isolator is a device made from a type of diode known as LED (light-emitting diode) specifically LASER or IR diode and a photosensor (a diode that senses light) to transfer the signal between two circuits.
There is no electrical connection between the two circuits. It is used for protecting a low voltage circuit from a high voltage circuit in case of a spike.
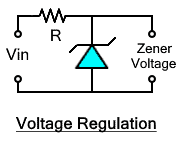
Voltage Regulation / Voltage Reference
A special type of diode known as Zener diode is used as a voltage reference in almost every electronic circuit. it is also known as a voltage regulator due to its ability to regulate voltage while offering current at a wide range. It works in reverse biasing to provide a stable voltage that can be used for biasing other electronic circuits that are sensitive to voltage fluctuation. Hence, voltage regulation is advantageous over other applications of diodes.
 Current Limiting
Current Limiting
A special type of diode known as a constant current diode or current limiting diode (CLD) is used for regulating the current flow through it.
Its function is to allow the current through it up to a predetermined level just like Zener diode allows a fixed voltage.
Oscillator
An oscillator is a circuit that produces continuous, repeated waveform. A diode such as a varactor and Gunn diode is used as an oscillator to generate the waveform.
The varactor diode or vericap diode has a junction with variable capacitance. This capacitance can be varied with reverse voltage which can be used in RF tuning circuit. Gunn diode operates in a negative resistance region where the current flow decrease with an increase in the voltage. Gunn diode is used in microwaves for generating high-frequency waves.
Related Articles:
- Photodiode: Types, Construction, Operation, Modes, Performance & Applications
- LED – Light Emitting Diode: Construction, Working, Types & Applications
AM Envelope Detector or Demodulator (Diode Detector)
AM or Amplitude modulation is a technique used for storing the information or the message signal in the envelope of a high-frequency signal or carrier signal. In order to get back the message signal (envelop) from the AM signal, we demodulate the signal.

Frequency Mixer
A frequency mixer is a circuit whose output is the sum or difference of any two frequency signals. Diodes can be used as a frequency mixer to shift the frequency of the signal. By doing so, we can modulate or demodulate any signal.
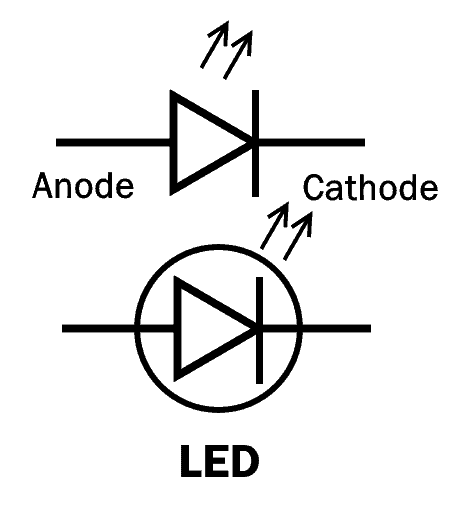
Light Source
A special type of diode known as LED (Light-emitting diode) is used for converting electric energy into light energy. Inside the PN junction of such diodes, when the electrons and holes meet, they release photons (light particles). There is an opening, a window for the light rays to come out.
Related Posts:
- Fast Recovery Diode? Symbol, Construction, Working & Applications
- Step Recovery Diode – SRD? Construction, Working & Applications
Diodes in Sensors
A sensor is an electrical component that converts any other type of energy into electrical energy. There are many different types of diodes. Some of these can be used as sensors as given below.
Temperature Sensor
According to the Shockley diode equation, the forward diode current depends on the temperature. According to the equation, if the forward voltage remains constant, any increase in the temperature decreases the forward current. Therefore, It can be used to sense the temperature.
Peltier or thermal diode is used for heat monitoring in microprocessors
Light Sensor
As the name suggests, photo sensor or light sensor are sensors that convert light energy into electricity. A photodiode is a light sensor that converts photons (light particles) into electricity. The photodiode has an exposed junction with a window. Photons enter through the window and hit the junction; it releases a pair of electron-hole. These electrons and holes flow out into the circuit generating potential across the diode terminals.

Solar Cell Photovoltaic Cell
A solar cell or photovoltaic cell is a source of energy that converts solar energy into electrical energy. Each solar cell is made of a diode to produce voltage when light struck its junction. It is a source of green energy.
Circuit Protection
Electronic circuits are very sensitive to voltage spikes and require protection to operate smoothly. Diodes offer such protection in circuits for their various feature. Some of them are given below.
Related Articles:
- PIN Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Point Contact Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
Reverse Current Protection
Reverse current protection is used to prevent the current from flowing backward which could damage the source or the components in a circuit. It is very important to block such current, especially in DC circuits.
Diode which is a unidirectional component is used for blocking any reverse current in a circuit.
Inductive Load Dissipation
As we know inductive loads store energy inside. When they switch off, the stored energy is released in form of high voltage spikes causing arcs across the switches. To prevent the circuit from such arcs, the inductive load must be dissipated internally. Diodes are used in an anti-parallel configuration known as the “flyback” configuration with the inductive load. This configuration lets the store energy cycle back into the inductor to dissipate it safely while protecting the source.
 Reverse Polarity
Reverse Polarity
As DC or direct current is unidirectional, a DC source has polarity i.e. positive and negative terminal. Therefore, In a DC circuit (such as batteries), the polarity of the source must be connected in the right configuration.

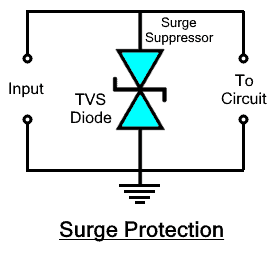
Surge Protection
Surges are high voltage spikes that sometimes occur in the line due to any unexpected event (such as thunderstorms & lightning). These surges can easily damage any component in a moment. A special type of diode known as TVS (transient voltage suppression) diode is used for suppressing high voltage spikes.
In short, there are additional uses of diodes, but we have discussed the major applications of diodes used frequently and vastly in electrical and electronic systems. Let us know in the comment box below if you want to add more value to the topic.
Related Resources:
- Constant Current Diode – Working, Construction, and Applications
- Varactor Diode – Symbol, Construction, Working and Applications
- Gunn Diode – Symbol, Construction, Working and Applications
- Avalanche Diode? Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Backward Diode: Construction, Operation, Characteristics and Applications
- Laser Diode? Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Tunnel Diode: Construction, Working, Advantages, & Applications
- Zener Diode – Symbol, Construction, Circuit, Working and Applications
- Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
- Difference Between Fast Recovery Diode and Step Recovery Diode
- Difference Between Schottky Diode and Fast Recovery Diode
- Difference Between Schottky Diode and Shockley Diode
- Difference between Photodiode and Photoresistor (LDR)
- Difference between LED and Photodiode
- Difference Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
- Diode Symbols – Electronic and Electrical Symbols
- Diode Formulas & Equations – Zenner, Shockley & Rectifier
- How to Test a Diode using Digital & Analog Multimeter – 4 Ways.
- Zener Diode & Zener Voltage Regulator Calculator
- Blocking Diode and Bypass Diodes in a Solar Panel Junction Box
- Simple Overvoltage Protection Circuit using Zener Diode








Hi, in the schematic, diodes as AND Gate, the diodes must be in the opposite direction.