How to Wire 240V Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
230V and 240V Continues Dual Element 9kW Electric Water Heater Thermostat Wiring
In the electric water heater and thermostat wiring series, we will be showing the continuous i.e. simultaneous wiring of dual heating elements (9000 Watts (each of 4500 Watts) and thermostats for 240V and 230V electric water heater. You may see the previsions post for 240V non-simultaneous water heater wiring installation.
As we have discussed before about the simultaneous (continuous) and non-simultaneous (non-continuous). In short words, the contentious or simultaneous thermostats and heating elements are operational at the same time supplied with power independently while in non-continuous (non-simultaneous), the upper heating element switch off when it completes the job and switch on the lower thermostat and heating element automatically due to the wiring configuration.
In this post, we will be showing a 9kW dual element (4.5kW heating element each) with 240V and 230V AC supply with thermostat and heating elements wiring for continuous operation i.e. both thermostats and heating element will be operational at once as they get separate power supply from the main distribution board.
Related Posts:
- How to Wire 240V Non-Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire a Single Element Water Heater and Thermostat?
240V AC Simultaneous Dual Element 9kW Water Heater Thermostat Wiring
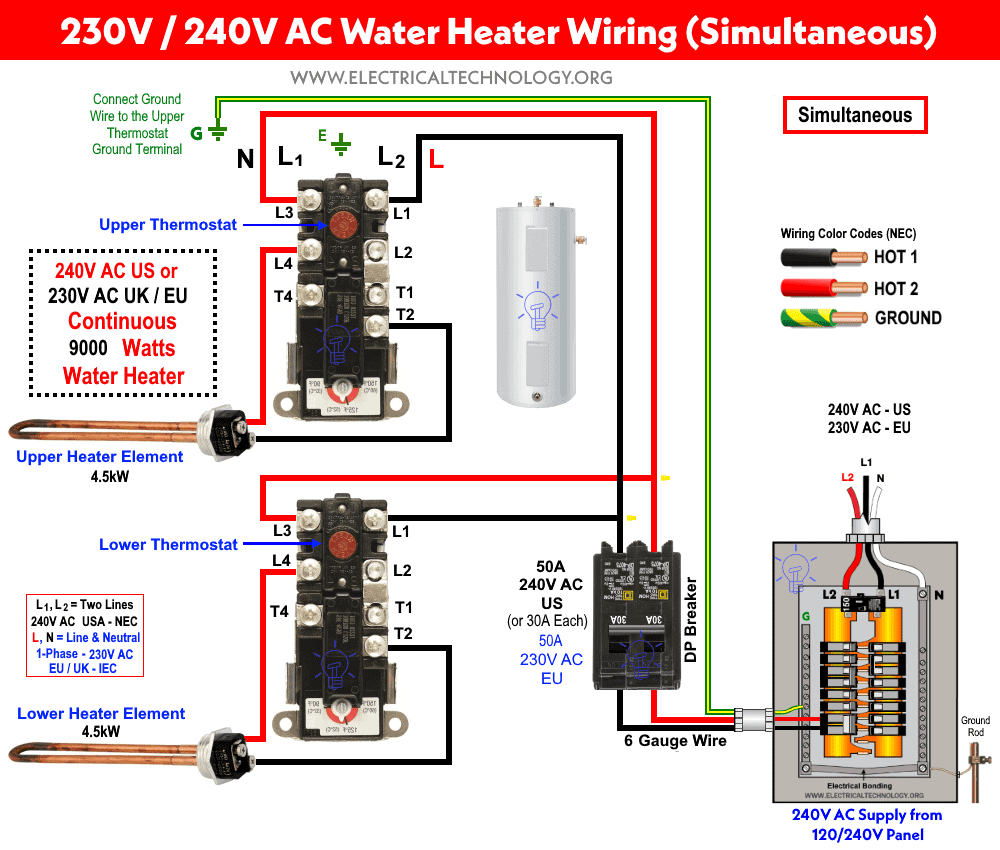
For 9000 watts simultaneous water heater wiring, we have used red and black wires as Line 1 and Line 2 for 240V AC and Line and Neutral for 230V AC respectively.
240V Simultaneous Wiring
Both Lines from the main 120V/240V panel as power supply are connected to the thermostats and heating elements. L1 is connected to the left side of both upper thermostat and lower thermostat L3 via 50 amperes circuit breaker and 45 to 50 amperes safety switches. The same power supply is connected to the lower thermostat and heating element followed by the same circuit breaker and switch. You may use two 30 amperes circuit breakers for two thermostats and heating elements instead of one 50 amperes circuit breaker.
Click image to enlarge
L4 and T2 terminals of both thermostats are connected to the upper and lower heater elements. In case of single circuit breaker (50A), a 6 gauge wire can be used where 10 gauge is suitable in case of two separate circuit barkers each of 30A.
Related Water Heater Wiring:
- How to Wire 120V Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire 120V Water Heater Thermostat – Non-Simultaneous?
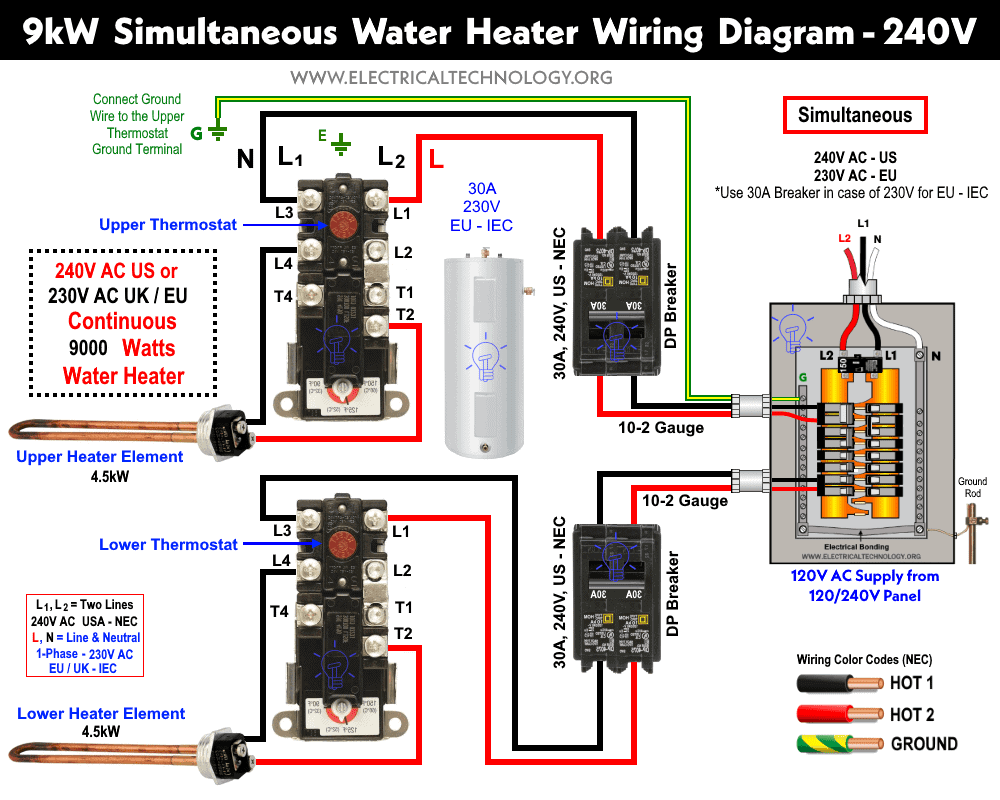
The following wiring diagram shows a 9000 watts water heater is wired for simultaneous operation where both thermostats and elements are connected to separate two poles circuit breakers each of 30 Amps.
Click image to enlarge
Related Heater Wiring:
- How to Wire 3-Phase Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire 3-Phase Non-Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
230V Simultaneous Wiring
Continuous Wiring connection of 230V single phase water heater is same as above for 240V where the only difference is that L1 and L2 are indicated by Line and Neutral Wires.
Circuit Breaker, Current and Switch Rating:
In case of 240V AC supply:
- Total wattage = 9kW Watts.
- Load Current = 9kW / 240V = 37.5A.
Since the breaker size should be 125% of total load current, therefore,
- 37.5A x 125%
- 37.5A x 1.25 = 46.875A
The nearest safe limit is 50A fuse or circuit breaker.
In other words, a 50A breaker with 240V supply can safely handle the 9000 watts. If we assume the 80% rating for smooth operation and future load, then:
- 50A x 240V x 80%
- 50A x 240V x 0.8 = 9600 Watts.
It means the system can safely handle a load of up to 9.6kW where our heater wattage is 9kW.
Note: Red color illustrates the Line or Phase wire and Black color shows the Neutral Wire in the above figures. You may follow your regional wiring color codes i.e. IEC or NEC.
Related Heater Wiring:
- How to Toggle Electric Water Heater Between 120V and 240V?
- How to Control Electric Water Heater using Switches?
- Disconnect the power before replacing, repairing, troubleshooting, maintenance and installation electrical appliances and equipment.
- Use the suitable voltage and ampere rating of switch with appropriate wire size and proper size of breaker according to the load rating.
- Failure to do so can result in electrical shock, serious injury, fire or even death.
- Please follow the manual instruction, local area codes or contact a licensed electrician for proper installation.
- The author will not be liable for any losses, injuries, or damages from the display or use of this information or if you try any circuit in the wrong format. So please! Be careful because it’s all about electricity and electricity is too dangerous.
Related Wiring Installation Tutorials
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Right Size Capacity of a Subpanel?
- Single Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in Home – NEC & IEC
- Three Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in Home – NEC & IEC
- How to Wire Auto & Manual Changeover & Transfer Switch – (1 & 3 Phase)
- How to Connect a Portable Generator to the Home Supply – 4 Methods
- How to Wire Analog and IP PTZ Camera with DVR and NVR?
- How to Wire Different Fire Alarm Systems – Conventional & Addressable
- Even More Residential Wiring Installation Tutorials







How would I calculate wattage for industrial band heater single phase & three phase?