Types & Characteristics of Surge Arresters
Surge Arresters – Types & Characteristics
Introduction
Atmospheric lightning phenomenon on overhead lines and bare conductors or metallic structures of an outdoors substation and over voltages due to switching operations of equipments and networks (switching over voltages) can cause serious hazards to equipment.
To protect the equipments and to aid insulation coordination surge arresters, also called “lightning arresters”, must be installed at overhead lines incoming or outgoing and close to transformers, because of their limited spatial protected zone.
Types & Characteristics of Surge Arresters
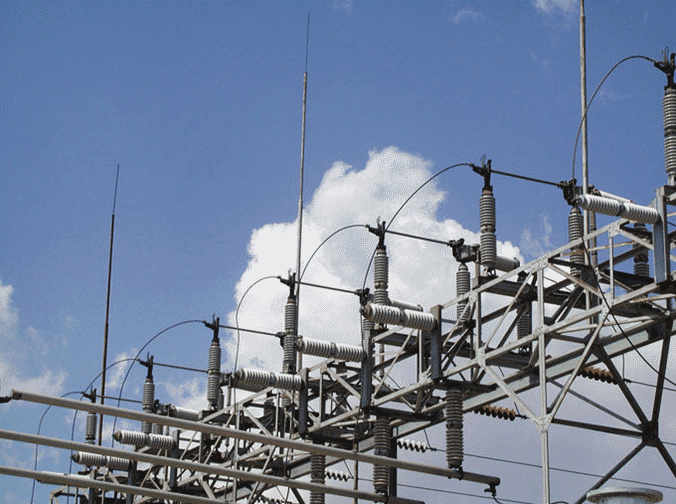
The most common surge arresters are non-linear metal oxide resistors type in aporcelain or silicone rubber housing, and are fitted in parallel with the object protected and connected to the earth grid.
Other construction type is silicon carbide (SiC) resistors (valve-type arresters).
Main electrical characteristics of surge arresters are:
- Resealing voltage (voltage across the arrester at which the follow current is still definitely interrupted after sparkover).
- Maximum continuous operating voltage (highest power-frequency – 50 Hz or 60 Hz – voltage that the arrester can withstand permanently).
- Rated short-circuit current
- Nominal discharge current, which common values are 5 kA, 10 kA and 20 kA.
Surge arresters are connected between the life conductors and the earth.
In installations with voltages above 52 kV surge arresters may be provided with “discharge operation counters”. Figure 1 shows an example of surge arresters.

Also Read: Overhead Lines Protection – Faults & Protection Devices
Additional Methods
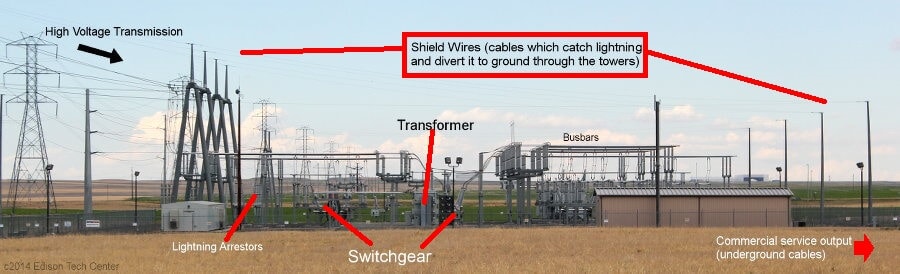
In overhead lines and outdoors substations above 52 kV is a common practice to install a lightning protection system that consists of ‘lightning rods’, ‘lightning aerial protection wires’ or a combination of both.

Also Read: Maintenance of Transformer – Power Transformers Maintenance, Diagnostic & Monitoring
LV Over voltages Protection
LV ( Low Voltage V ≤ 1 kV ) equipment, namely electronic and informatics equipment, may suffer severe damages due to lightning discharges through the cables or through the building structure.
To prevent those damages it is usual to install in LV switchboards ‘power surge protectors’ (SPD), with standard nominal discharge currents of 5 kA, 10 kA and 20 kA, although some models may reach values of 30 – 70 kA.
Similar to the surge arresters these devices are connected between the live conductors and the earth, as shown in Figure 4.





Thank you for taking the time.
Best regards,
Thomassen Valenzuela
This was very useful and I benefited a lot from this article. I liked this article very much