How to Find Power, Voltage & Ampere Rating of Outlet, Receptacle and Plugs
How to Find the Voltage, Power and Ampere Ratings of Outlet, Switch, Receptacle, Socket and Plugs etc.?
Switches, outlets, plugs, receptacles, connectors, breakers, GFCI, RCD’s etc., are designed and rated with various electrical characteristics. The rating of an outlet and switch depends on multiple factors, such as the material and insulation class used for the switch contacts, the size and spacing between the contacts, and the specific application.
There are three main ratings of outlet, switches and plugs:
- Current Rating: The current rating, indicated in amperes on the switch nameplate, shows the maximum amperes the switch can safely carry to the connected load circuit.
- Voltage Rating: This is the maximum voltage at which a switch can be safely used and installed in a circuit.
- Power Rating: It shows the maximum wattage rating of outlet, switch or plug which they can hold and handle safely.
Now, let’s explore the rules and regulations regarding switch ratings and how to select the proper size of a switch based on power, current and voltage capacity.
Ratings of Standard Outlets and Switches
US & CA
In the United States and Canada, the most common ampere ratings for electrical outlets in residential applications are 15A and 20A, operating at standard voltages of 120V and 240V single-phase AC. Examples of 15A are NEMA 14-15R, 5-15R, 6-15R and 14-50R etc. Example of 20A outlets are NEMA 2-20R, 5-20R, 6-20R, 14-20R.
- Both 15A and 20A outlets are used in 120V and 240V circuits.
- A 15A outlet at 120V can handle 1,800 watts, and 3,600 watts at 240V.
- A 20A outlet at 120V can handle 2,400 watts, and 4,800 watts at 240V.
- A 15A outlet and switch are typically used for small appliances and non-continuous loads in bedrooms and general areas, such as lighting and electronic devices (e.g., TVs).
- A 20A outlet and switch are used for heavy-duty appliances in kitchens (e.g., microwaves), as dedicated circuits for single devices, and for power tools and appliances in locations such as laundry rooms, garages, and bathrooms.
- The suitable wire size for 15A outlets is #14 AWG, while #12 AWG is used for 20A outlets, as per NEC Table 310.15(B)(16).
According to the National Electrical Code (NEC) 210.19(A), only 80% of the rated outlet, switch, or breaker capacity should be used for continuous load circuits (which last for 3 hours or more). Thus: Warning UK In the United Kingdom, the standard ampere rating for electrical socket outlets in residential applications is 13A at 230V single-phase AC. Such example outlet and plug is BS 1363 where the wire size is 1.5 mm2 or 2.5 mm2 based on the load circuit. EU In Europe and other IEC-compliant countries, the standard ampere rating for electrical socket outlets in residential applications is 16A at 230V single-phase AC. AUS/NS In Australia and New Zealand, the standard ampere rating for electrical socket outlets in residential applications is 10A at 230V single-phase AC. All switches, outlets, receptacles, plugs, connectors, breakers, wires, etc., have two amperage ratings: the maximum current rating and the safe maximum current rating. A switch or outlet can be used at its maximum amperage rating for non-continuous load circuits, such as lighting points. For instance, a 15-amp switch or outlet is rated for a maximum of 15 amps, meaning it can be wired and installed for a 15A non-continuous general lighting circuit. The maximum current rating depends on the circuit voltage and should never be exceeded. If it does exceed the rated current, the switch’s contacts may melt and weld together, rendering the switch unusable. Without a breaker, this can also damage connected devices and potentially cause a fire. In simple terms, a 15A switch or outlet should not be used to handle a 20A load. Typically, residential devices run on 15A (14-gauge) circuits, but occasionally, 20A (12-gauge) devices are used with a single-phase 120V AC supply. For 240V AC supply, 30A (10-gauge) circuits are commonly used, depending on the device wattage, such as water heaters. Most residential devices are 15A, though occasionally, a 20A device may be used. A switch or outlet can safely carry 80% of its rated current for continuous loads, such as water heaters, as per NEC 210.19(A). For example, the safe maximum current of a 20-amp switch or outlet is 16 amps, meaning it can be wired and installed for a 16A continuous load circuit. Safe Current Calculation: Safe Maximum Current = Maximum Current × 80% Related Switch Wiring Tutorials: Example: What is the safe maximum current for a 15A switch? Solution: This means a 15A switch can safely handle a 12A load. Although it can carry a 15A load for non-continuous use, for continuous loads, a 15A switch should only carry a maximum of 12A. If the current rating is the same for both 120V and 240V, the power in volt-amperes (VA) or watts (W) will differ. For example: Similarly, the safe maximum current for a 15A switch is 12A, and the load it can handle is 12A × 120V = 1,440W. The current rating of outlet and switch is usually printed on the back. It can also be identified by the rated breaker used with the outlet or the wire size. Additionally, the physical appearance of outlets can help distinguish between them; for example, a 120V outlet typically has two vertical slots, while a 240V outlet has one T-shaped slot in the two vertical slots.
Related Calculators: Voltage rating of an outlet or switch shows the maximum allowable voltage of the circuit where the switch has to be used for different loads. A switch can be rated for AC voltage, DC voltage or both having different values and ampacity. For example, a switch can be rated for 240V AC, 230V AC, 15 Amps, 120V DC, 20A etc. The wall switches in the United states are generally rated for 120V to 277V AC. Read the user manual or nameplate data on the switch before installation. The supply voltage should never exceed the voltage rating of switch. In other words, If we connect an 120V switch on 500V, the applied voltage may jump over the open contacts (and overheat due to overvoltage) of the circuit and connect the load to the supply voltage. It will lead to spark as well which may cause fire. The breaker will open the circuit and stop the operation if current exceed the limit due to excessive voltage as compared to the rated voltage. In short, an 120V and 230V rated switches should not be used for 240 and 480V respective.
A switch and outlet rated for: The power capacity of a switch and outlet can be calculated using the following formula:
Using this formula, To find the rating of an electrical outlet, follow these steps: Most outlets have their rating information stamped or engraved on the face or back. This typically includes: These markings indicate the maximum load the outlet can handle safely. The physical design of the outlet can give clues about its rating: The circuit breaker connected to the outlet’s circuit provides insight into the outlet’s rating. If the breaker is rated for 20 Amps, the outlet is likely rated for 20 Amps, unless it was installed incorrectly. Always ensure the outlet matches the breaker’s capacity. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage across the outlet. In the U.S., standard household outlets typically supply 120V, while larger appliances might use 240V outlets. Make sure the outlet voltage matches the expected rating. Look at the wiring gauge connected to the outlet. For example: The National Electrical Code (NEC) has specific guidelines on outlet ratings based on the breaker size and wiring. For example: By following these steps, you can determine the rating of an outlet safely and accurately. US – NEC The standard outlets and receptacles used for common household applications in the US is 15A and 20A. Here are some common standard and non-standard outlets for both NEC and IEC. UK and IEC following countries Related Posts: For 15A and 20A circuit, use 14 and 12 gauge wire respectively. In case of outdoor, laundry, kitchen, bathroom or watery areas, it is the code to use GFCI and ground fault interrupting receptacles for maximum protection. Disconnect Switch Rating According to the article and section of NEC-430: Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Rating Example: What is the proper size of ATS for a 210kW, 208V three phase AC supply. Solution: You may use then 600A (three poles) automatic transfer switch for 210kW heating loads. Related Posts: Ampere Rating of Outlet and Receptacle: Maximum Cord and Plug Load: Receptacle Ratings: Receptacle Ratings for Ranges: Wire Gauge for Switches, Plugs, and Outlets: Voltage and Current Compatibility: Switch Wiring: Switch and Circuit Rating Compatibility: Plugging Devices into Outlets: Switch Ratings: IP Rated Switches: RCD Protection: Earth Pin Requirement: Proper Protection: Inductive Load Compatibility: Proper Heights for Installation: Related Posts: FAQs Can a 15A Outlet and Switch be Used on 20A Breaker? Yes. According to NEC Code, It is allowed to use 15-amp outlets and switches on a 20-amp breaker. Can a 20A Outlet and Switch be Used on 15A Breaker? NO. It is against NEC Code to use 20-amp outlets and switches on a 15-amp breaker. Can a 120V Outlet and Switch be Used on 240V Circuit? Yes. According to NEC Code, It is allowed to use 120V outlets and switches in a 240V supply. Can a 240V Outlet and Switch be Used on 120V Circuit? NO. NEC doesn’t allow to to use 240V outlets and switches in a 120V supply. Related Post: Electrical Installations – Standards & Regulation around the World
Current Rating of Outlets and Switches
Maximum Current:
Safe Maximum Current:
(Note: This is an example calculation. For 240V supply, use 30A switches, plugs, and outlets.)
Voltage Rating of Outlet and Swatch
Power Rating of Outlets and Switches
How to Find the Rating of an Outlet and Switch?
1. Check the Outlet’s Markings:
2. Examine the Shape and Configuration:
3. Check the Breaker:
4. Measure Voltage:
5. Wiring and Cable Inspection:
6. Reference NEC Standards:
Standard & Non Standard Size Outlets and Plugs
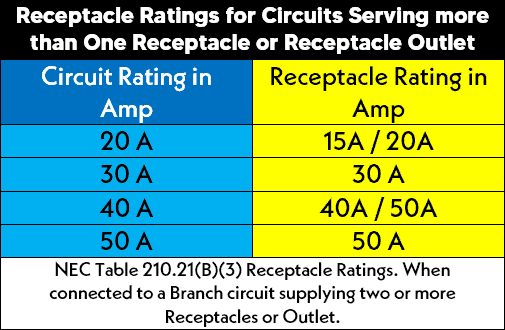
How Many Switches, Receptacles and Socket-outlet Can be installed on 15A & 20A Circuits?
Sizing ATS and Disconnect Switches
NEC and IEC Rules about Outlet, Receptacle, Socket and Switches Ratings
It is against regulations to wire the switch on the neutral conductor.
Safety Precautions
Resources:









This is the best site of technology
A switch rated for 15A, 120V can be used on 20A, 120V circuit from the distribution board.
A switch rated for 20A, 120V can’t be used on household 15A, 120V supply circuit.
i think must be vice versa according to this…
15A devices (load) can be plugged into a 20A outlet, but not vice versa.
it was just a confusion.
it is clear now, my appreciation to this site.