What is the Main Difference between Avalanche Diode and Zener Diode?
Zener diode and avalanche diode are two different types of diodes used in electronic circuits for protection. Both of them are PN junction diodes designed to operate in reverse breakdown regions. However, that is as far as their similarities go.
Other than that they are quite different in characteristics, structure, applications, etc. This article explores the differences between Zener diode and avalanche diode.
Before going into the list of differences between the Zener diode and Avalanche diode, let’s discuss some of its basics first.
Related Posts:
What is a Diode?
A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device that allows current flow in only one direction. It is made up of the combination of a P-type semiconductor and N-type semiconductor layer to form a PN junction. It is widely used for switching and protection in electrical circuits.
The PN junction creates a gap that is free of charge carriers called a depletion region. The depletion region acts as an insulator. However, its width increases or decreases with the applied voltage and its polarity. In forward bias, the depletion width decreases and the diode conducts current while in reverse bias, the depletion width widens and blocks the flow of current.
There are several different types of diodes where Zener diode and avalanche diode are one of them.
Related Posts:
Zener Diode
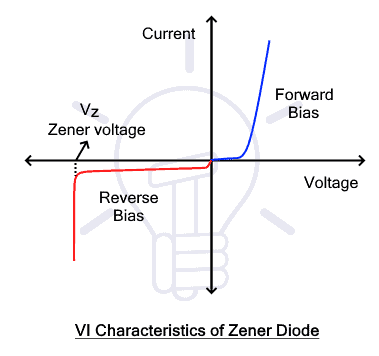
A Zener diode is a type of PN junction diode that is designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region. It can conduct in both forward and reverse directions. In forward bias, it acts as a conventional diode and conducts current.
While in reverse bias it does not conduct until applied voltage reaches the reverse breakdown region called Zener region. It safely conducts large current in the zener region without any damage to limit the voltage across it.
Zener diode is designed to operate in reverse bias and it is used to regulate voltage in electronic circuits. The doping concentration determines the Zener voltage of the diode. It’s the reverse bias voltage across the diode that it can maintain while the current varies. However, the Zener diode is used for low-power applications.
Zener Effect: Zener diode working principle is based on Zener Effect. The Zener effect occurs in the Zener diode when a high reverse voltage is applied. Since it already has a very narrow depletion width due to high doping concentration, the reverse voltage generates a high electric field across it.
This electric field accelerates the free minority carriers that tunnel from the valance band of the P-type semiconductor to the conduction band of the N-type semiconductor. This generates more charge carriers causing a large reverse current.
Zener breakdown is a safe method and does not damage the device until the current that flows through the diode does not exceed the limit.
Related Posts:
- Difference between Photodiode and Photoresistor (LDR)
- Difference Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
Avalanche Diode:
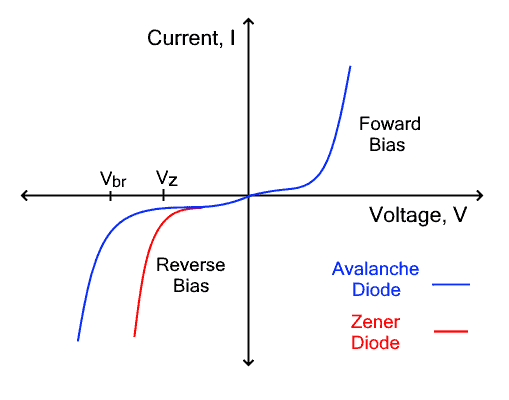
An Avalanche diode is a type of PN junction diode designed to operate in a reverse breakdown region. In reverse bias, it operates like a conventional diode with a small reverse leakage current until the voltage exceeds the reverse breakdown voltage.
Avalanche breakdown occurs at this voltage, at which the diode conducts heavy current. Comparatively, the avalanche voltage is very higher than the Zener voltage. Therefore avalanche diode is used for protection against high-voltage transients. It is suitable for high voltage and high current applications such as surge protectors etc.
The Avalanche diode works on the principle of the avalanche effect. The avalanche effect occurs in every diode. It occurs when high reverse voltage is applied creating a strong electric field that pushes the free electrons to move through the junction.
The electrons collide with more atoms, thus releasing more free electrons and generating a large current flow. The avalanche breakdown is destructive in normal diodes whereas the high doping concentration of avalanche diode prevents it by eliminating the hot spots and carrier concentration. The doping concentration also determines the avalanche breakdown voltage.
Related Posts:
Key Differences Between Zener and Avalanche Diode
The following table shows the comparisons between the Avalanche and Zener diode.
| Zener Diode | Avalanche Diode |
| A Zener diode is a type of diode used to regulate voltage using the Zener effect in reverse bias. | An Avalanche diode is a type of diode used to prevent voltage surges using the avalanche effect in reverse bias. |
| It works on the Zener Effect which allows current due to the tunneling of electrons from the valance band of the P-type to the conduction band of the N-type semiconductor. | It works on the avalanche effect in which a high electric field forces electrons to accelerate and collide with other atoms to generate more electrons and reverse current. |
| It has a high doping concentration. | It has a low doping concentration. |
| It has a thin depletion region | It has a large depletion region. |
| It cannot handle high voltage. Thus it has low ratings. | An avalanche diode can easily handle large voltages. |
| The Zener diode is a low-power component | The Avalanche diode is a high-power component. |
| It has a negative temperature coefficient | It has a positive temperature coefficient |
| It is more reliable and precise in voltage regulations. | It is unreliable for voltage regulation but great for surge protection |
| The Zener diode generates low noise. | The avalanche diode generates avalanche noise. |
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Fast Recovery Diode and Step Recovery Diode
- Difference Between Schottky Diode and Fast Recovery Diode
Comparison Between Zener & Avalanche Diodes
Working Principle
- Zener diode operation is based on the principle of the Zener effect.
- Avalanche diode operation the based on the principle of the avalanche effect.
Function
- The Zener diode is mainly used for voltage regulation.
- An Avalanche diode is used for protection against high-voltage surges.
Doping Concentration
- Zener diode has a very high doping concentration.
- The Avalanche diode has a lower doping concentration.
Depletion Region
- Zener diode has a thin depletion region.
- The Avalanche diode has a wide depletion region.
Voltage Ratings
- A Zener diode is used for low voltages and designed to operate at zener voltage ranging A 5V to 200V.
- An Avalanche diode is used for high voltages ranging up to several kilovolts.
Current Handling
- Zener diode cannot handle large currents.
- Avalanche diode can withstand high voltage as well as large currents.
Power Rating
- Zener diode has a lower power handling capability
- While avalanche diode has higher power handling capabilities.
Temperature Coefficient
- The Zener diode has a negative temperature coefficient i.e. its zener breakdown voltage decreases with an increase in temperature. Furthermore, it is very small which makes its value more stable and best for precise voltage regulation
- An Avalanche diode has a positive temperature coefficient i.e. its avalanche breakdown voltage increases with an increase in temperature. Also, its coefficient is larger than zener making it relatively less reliable for voltage regulation.
Noise
- The Zener diode generates less noise as compared to the avalanche diode.
- The Avalanche diode generates more noise. It even has its own name called avalanche noise generated due to the avalanche effect.
Response Time
- The Zener diode has a very fast response time.
- The Avalanche diode has a relatively slow response time.
To conclude this topic, we can say that the zener diode and avalanche diode both are designed to operate in reverse breakdown regions but the Zener is used for voltage regulation in low power circuits while the avalanche diode is used for voltage surge protection in high voltage circuits.
Related posts about the comparison and differences between different electrical and electronic components and devices.
- Difference Between Phototransistor and Photoresistor (LDR)
- Difference Between JFET and MOSFET
- Difference Between BJT and FET Transistors
- Difference Between Transistor & Thyristor (SCR)
- Difference Between NPN and PNP Transistor
- Difference Between Voltage Source and Current Source
- Difference between Voltage Source Inverter & Current Source Inverter
- Difference between Inverter & UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply
- Difference Between Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifier
- Difference Between Amplifier and Operational Amplifier
- Difference Between Encoder and Decoder
- Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- Difference Between 8085 & 8086 Microprocessor – Comparison
- Difference Between RAM and ROM – Comparison
- Difference Between CPU and GPU – Comparison
- Difference between Active and Passive Components
- Difference Between Multiplexer (MUX) & Demultiplexer (DEMUX)
- Main Difference Between Sensor and Actuator
- Main Difference between Sensor and Transducer
- Difference Between Digital Latch and Flip-Flop Circuits


 Why You Should Never Buy or Use Male-to-Male Extension Cords
Why You Should Never Buy or Use Male-to-Male Extension Cords Why is the Neutral Wire Size Smaller than the Phase Wire?
Why is the Neutral Wire Size Smaller than the Phase Wire? Why is the Ground Wire Size Smaller than the Hot Wire?
Why is the Ground Wire Size Smaller than the Hot Wire? Appliances You Should Never Plug Into an Extension Cord
Appliances You Should Never Plug Into an Extension Cord Why Do We Need a GFCI & How Does it Protect During Faults?
Why Do We Need a GFCI & How Does it Protect During Faults? How Does a Standard Breaker Respond to Electrical Fault?
How Does a Standard Breaker Respond to Electrical Fault?