Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent (RCBO) – Construction, Types, Working and Applications
What is An RCBO?
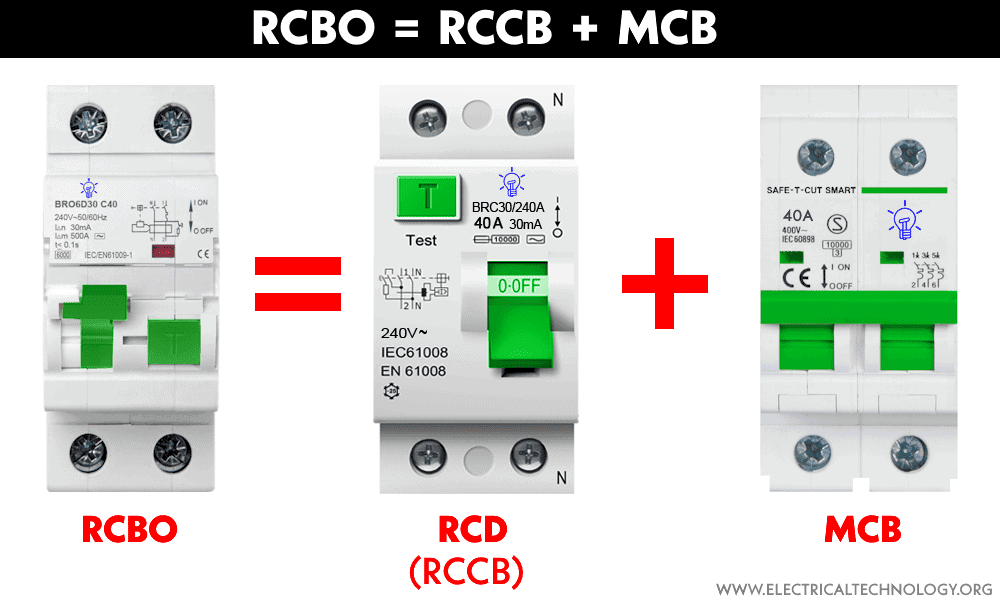
An RCBO, or Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent, is a type of electrical protection device used to protect electrical circuits and equipment from both overcurrent and earth faults. Alternatively, An RCBO combines the functions of a Residual Current Device (RCD or RCCB) and a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) in a single unit to provide protection against both short circuits and leakage current.
In simple terms
RCBO = RCD + MCB
This way, the RCBO offers:
- RCD Function: The RCD component of an RCBO is designed to detect and interrupt the circuit when it senses a residual current, which is an imbalance between the outgoing and incoming currents. This imbalance can occur in the presence of a fault, such as a ground fault or leakage current, which could potentially lead to electric shock.
- MCB Function: The MCB function serves to protect the circuit against overcurrents and short circuits. It automatically trips or opens the circuit when it detects an excessive current flowing through it, preventing damage to the connected devices or wiring circuits.
Importance of An RCBO
In conventional protection where both MCB and RCCB are used, in the case of an earth fault, the RCCB (RCB) will trip and disconnect the entire downstream circuit until the issue is resolved.
In the case of a fault on a dedicated circuit, the RCBO will only disconnect the affected circuit. Hence, the rest of the circuit will work properly and smoothly. In addition, it saves extra space in DB/consumer units because you only need to use one RCBO unit instead of two separate units for RCD and MCB.
The necessity of an RCBO emerges because an MCB only protects a circuit against short circuits and overcurrents, while the RCD and RCCB interrupt the circuit in case of residual current (leakage, i.e., earth fault currents). Therefore, using a single unit that combines the advantages of both overcurrent and leakage current protection is the suitable approach to prevent electric shock and hazardous fires.
- Related Post: What is an RCD (Residual Current Device)? – RCB and RCCB
Characteristics & Features of of RCBOs
- Dual Functionality:
- Combines the functions of a Residual Current Device (RCD) and a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) in a single device.
- Protects against both earth fault currents (residual current) and overcurrents.
- Residual Current Protection:
- Detects imbalance between incoming and outgoing currents, triggered by leakage to earth.
- Provides protection against electric shock caused by ground faults, such as faulty appliances or damaged wiring.
- Overcurrent Protection:
- Protects against excessive currents flowing in the circuit due to short circuits or overloads.
- Trips the circuit breaker to disconnect the load in case of overcurrent conditions.
- Sensitivity Adjustment:
- Some RCBOs allow for adjustable sensitivity settings to accommodate different applications and environments.
- Sensitivity adjustments are typically expressed in terms of milliamps (mA) for the residual current protection.
- Tripping Speed:
- RCBOs are designed to trip quickly in the event of a fault to minimize the potential for electric shock or fire hazards.
- For 30mA tripping current, the tripping speed is 300ms. For 10mA tripping current, the tripping speed is 40ms.
- Current Ratings:
- Common sensitivity values are 30 mA (milliamps) for general purposes and 10 mA for additional protection in sensitive environments.
- Common current ratings include 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 32A and and 40A, among others.
- Voltage Ratings:
- Typically designed for specific voltage systems, such as 230V or 400V, depending on the electrical distribution system.
- Compatibility:
- RCBOs are designed to be compatible with standard electrical systems and are used in conjunction with other circuit protection devices such as MCBs, MCCBs, RCDs, ELCBs etc.
Construction of RCBO
As illustrated in the internal structure of an RCBO in the following figure, it clearly shows that an RCBO is nothing special but a combination of an MCB and RCD in a single box. Hence, the MCB unit safeguards the circuit against overload and short-circuit, while the RCD unit protects the circuit against leakage and earth fault currents.
The figure on the right side shows an RCBO based on an electromechanical relay and operating mechanism. The figure on the left side shows an advanced RCBO based on an electronic relay (PCBA). The common parts of the RCBO are as follows:
- RCD Test Button
- Toggle – Operator Handle
- Residual Earth Trip Indicator
- Electromechanical Relay
- Electronic Relay (PCBA)
- Fixed Contact
- Moving Contact
- Operating Mechanism
- Arc Chamber
- Solenoid (Coil)
- Thermal Protection Bimetal
- DIN rail holder clips
- Upper Terminal (Incoming Supply)
- Lower Terminal (Outgoing Load)
- Toroid Core Transformer – Main, Neutral & Search Coils (Electromagnetic Circuit)
Operation of an RCBO
an RCBO works by continuously monitoring the current flow in a circuit, detecting imbalances and overcurrent that indicate faults, and tripping the circuit to disconnect the power when necessary.
- Residual Current Detection (RCD Function):
- An RCBO constantly monitors the flow of current in the circuit.
- In a normal operating condition, the current flowing into the circuit should be equal to the current flowing out (Kirchhoff’s Current Law).
- The residual current is the difference between the incoming and outgoing currents. An imbalance indicates a fault, such as a leakage to earth.
- Overcurrent Protection (MCB Function):
- In addition to residual current protection, the RCBO also functions as a traditional circuit breaker.
- It protects against overcurrent conditions caused by short circuits or excessive loads in the circuit.
- If the current exceeds the rated threshold, the overcurrent protection mechanism is triggered.
- Operating Mechanism:
- The operating mechanism of the RCBO is responsible for tripping the circuit in the event of a fault.
- In an electromechanical RCBO, an electromagnet is used to trip the device when an overcurrent or residual current fault is detected.
- In an electronic RCBO, a solid-state electronic circuit is employed to sense and respond to faults.
- Arc Chamber:
- In the case of a short circuit, an arc may form between the contacts when they separate during the tripping process.
- The arc chamber in an RCBO is designed to contain and extinguish the arc safely.
- Resetting and Test:
- After a trip event, most RCBOs have a reset mechanism that allows the user to restore power to the circuit after the fault has been addressed.
- A test button is often provided to simulate a fault and ensure the proper functioning of the RCBO’s tripping mechanism.
Types of RCBOs
Residual Current Circuit Breakers with Overcurrent Protection (RCBOs) come in various types, each designed to meet specific application requirements. The main types of RCBOs include:
- Electromechanical RCBOs:
- These RCBOs use electromechanical components, such as an electromagnet, to detect and respond to overcurrent and residual current faults.
- Electromechanical RCBOs are known for their reliability and durability.
- Electronic RCBOs:
- Electronic RCBOs utilize solid-state electronic components, including microprocessors and sensors, to detect and respond to faults.
- They often offer advanced features, such as adjustable sensitivity settings and more precise trip time characteristics.
- Time-Delayed RCBOs:
- Time-delayed RCBOs have a built-in delay before tripping in response to overcurrent or residual current faults.
- This delay allows for temporary current surges, such as those caused by motor starting, without triggering an unnecessary trip.
- Adjustable Sensitivity RCBOs:
- Some RCBOs allow users to adjust the sensitivity level for the residual current protection.
- This feature is useful in situations where a higher or lower sensitivity is required based on specific applications or environmental conditions.
- AC and A Types:
- RCBOs are categorized into AC type and A type based on their sensitivity to different types of residual currents.
- AC type is suitable for general applications and provides protection against sinusoidal alternating currents.
- A type is more sensitive and designed to protect against both sinusoidal and pulsating direct currents, making it suitable for additional protection in sensitive environments
- Three-Phase RCBOs:
- Three-phase RCBOs are designed for use in three-phase electrical systems.
- They provide protection against overcurrent and residual current faults in each phase.
- Portable RCBOs:
- Portable or plug-in RCBOs are designed to be plugged into existing electrical outlets, providing an additional layer of protection for specific devices or appliances.
- They are commonly used in residential settings for added safety.
- Combination RCBOs:
- Combination RCBOs integrate additional features or functions, such as surge protection or communication capabilities, into a single device.
- Related Post: Types of Circuit Breakers – Working and Applications
When selecting an RCBO, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of the electrical system and the level of protection required for the connected loads. Different types of RCBOs cater to diverse applications and can be chosen based on factors like sensitivity, delay characteristics, and environmental considerations.
Good to know:
- “Type A” RCDs are not suitable for single phase electronics and IT systems because they do not detect smooth DC.
- Type AC RCBOs must be connected downstream of Type A, F, B or EV RCDs.
- 1P + N – 230V single phase RCBOs are not suitable for electronic and sensitive applications).
- 3P + N – 415V three phase – 4-wire system must be used with Neutral wire.
Applications of RCBOs
Residual Current Circuit Breakers with Overcurrent Protection (RCBOs) serve mainly two functions viz short-circuit / overcurrent and leakage/earth fault protection in electrical installations and applications.
In residential, commercial and industrial installations, RCBOs are commonly used in consumer units and electrical panels to safeguard individual circuits, providing combined overcurrent and residual current protection for lighting, appliances, and socket-outlets etc.
- Related Post: Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCD
FAQs
1. What is an RCBO?
- A Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection (RCBO) is a device that combines the functions of a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) and a Residual Current Device (RCD) in a single unit. It provides protection against overcurrents, short circuits, and earth leakage currents.
2. How does an RCBO work?
- An RCBO continuously monitors the electrical circuit for imbalances in current flow. It responds to both overcurrent conditions and residual current faults. The MCB component protects against overloads and short circuits, while the RCD component safeguards against leakage and earth faults.
3. What is the purpose of adjustable sensitivity in an RCBO?
- Adjustable sensitivity allows users to customize the level at which the RCBO responds to residual current faults. This feature is useful in adapting the device to different applications and environments where specific sensitivity levels may be required.
4. Are there different types of RCBOs?
- Yes, RCBOs come in various types, including electromechanical and electronic versions, time-delayed RCBOs, adjustable sensitivity RCBOs, AC and A types, three-phase RCBOs, portable RCBOs, and combination RCBOs. Each type is designed to meet specific application needs.
5. What is the difference between AC and A type RCBOs?
- AC type RCBOs provide protection against sinusoidal alternating currents, suitable for general applications. A type RCBOs are more sensitive and offer protection against both sinusoidal and pulsating direct currents, making them suitable for environments with additional sensitivity requirements.
6. Can an RCBO be used in a three-phase electrical system?
- Yes, there are three-phase RCBOs specifically designed for use in three-phase electrical systems. They provide protection against overcurrents and residual currents in each phase.
7. How do I test if my RCBO is functioning correctly?
- Most RCBOs come equipped with a test button. Pressing this button simulates a fault condition, allowing you to verify that the RCBO trips as expected. Regular testing is essential to ensure the continued reliability of the device.
8. Can I use an RCBO as a standalone device for circuit protection?
- Yes, an RCBO can function as a standalone device for comprehensive circuit protection, combining both overcurrent and residual current protection in a single unit.
9. What is the purpose of a time-delayed RCBO?
- Time-delayed RCBOs have a built-in delay before tripping, which allows for temporary current surges, such as those caused by motor starting. This feature prevents unnecessary tripping during normal, temporary overcurrent events.
10. Are there any specific safety considerations when installing an RCBO?
- It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and ensure that the RCBO is installed by a qualified electrician. Regular testing and maintenance are recommended to verify proper functionality and reliability over time.
Bonus: Additional Premium Resources for RCBOs & RCDs Wiring Tutorials
- How to Wire an RCBO? Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent
- How to Wire 1-Phase Split Load Consumer Unit? – RCD+RCBO
- How to Wire 230V Dual Split Load Consumer Unit? – RCD+MCB
- How to Wire Single-Phase, 230V Consumer Unit with RCD? IEC, UK & EU
- Wiring of the Distribution Board with RCD (Residual Current Devices)
- How to Wire a Garage Consumer Unit?
Related Posts:
- Air Circuit Breaker (ACB): Construction, Operation, Types and Uses
- SF6 Circuit Breaker – Types, Construction, Working and Applications
- Tripping Curves of Circuit Breakers – B, C, D, K and Z Trip Curve
- HVDC Circuit Breaker – Types, Working and Applications
- Electronic Circuit Breaker – Schematic and Working
- Smart Wi-Fi Circuit Breaker – Construction, Installation and Working
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Read MCB Nameplate Data printed on it?
- Why Circuit Breaker Capacity Was Rated in MVA and Now in kA and kV?
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
- Can We Use AC Circuit Breaker for DC Circuit and Vice Versa?
- AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
- GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications

 Why is the Long Prong Neutral Instead of the Narrow Prong?
Why is the Long Prong Neutral Instead of the Narrow Prong? Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet? Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs?
Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs? How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection?
How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection? How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection
How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables?
How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables?