Effects of Temperature on Sag in an Overhead Line
The sag in an overhead line, which refers to the vertical distance between a conductor and the straight line between its two supports, is affected by temperature changes. The sag and stresses of line conductors change in response to temperature fluctuations due to thermal expansion and contraction. The effects of temperature (neutral phenomena i.e. sunlight, snow and ice coating, wind) on sag in overhead lines are as follows:
Temperature Increase:
-
- When the temperature of the conductor increases, the conductor expands. As the conductor expands, its length increases, leading to a decrease in sag. This is because the conductor becomes longer, and the distance between the supports effectively increases.
Temperature Decrease:
-
- Conversely, when the temperature decreases, the conductor contracts. As the conductor contracts, its length decreases, resulting in an increase in sag. In colder conditions, the conductor becomes shorter, and the distance between the supports effectively decreases.
Thermal Expansion Coefficient:
-
- The material of the conductor plays a crucial role. Different materials have different coefficients of thermal expansion. The coefficient of thermal expansion is a measure of how much a material expands or contracts for a given temperature change. Conductors with higher thermal expansion coefficients will experience more significant changes in sag for a given temperature change.
Sag Tension Relationship:
-
- The relationship between sag and tension in the overhead line is influenced by temperature. The sag-tension relationship is typically represented by a curve. Changes in temperature can shift this curve, affecting the sag at a given tension level.
- The curves and equations for sag-tension relationship can be seen in the detailed post on “Sag in overhead powerlines” Where sag calculations are provided for situations where structures and poles are at equal and unequal levels, as well as the effects of ice and wind on span and tension (sag) in overhead lines.
Compensation Devices:
-
- Overhead lines often incorporate devices such as compensators or automatic tensioning systems to counteract the effects of temperature on sag. These devices help maintain the desired tension and sag levels, ensuring the proper functioning and safety of the overhead line.
Good to know:
Sag when Structures are at equal levels:
Sag when Structures are at unequal levels:
Wind pressure on lines:
Density of Ice on lines:
Vertical sag in the conductor:
SV = S Cos θ
Where:
- S = Sag
- L = Span (distance between poles) in meters
- W = Weight of conductor
- T = Tension in lines
- t = Thickness of ice coating around the conductor
- d = diameter of conductor
Understanding and managing the effects of temperature on sag is crucial in the design, installation, and maintenance of overhead power lines to ensure their reliability and safety. Engineers consider factors such as the conductor material, thermal expansion coefficients, environmental conditions and local area codes to design and determine the appropriate sag-tension relationship based on standard ground clearance of sag for a given application.
Related Posts:
- What is the Minimum Ground Clearance for Overhead Power Line?
- What is the Power Angle in a Power Transmission Line?
- Why are Overhead Power Lines Loose on Electric Poles & Towers?
- How Many Poles and Towers are Situated Within a 1-km Span?
- Why are Overhead Power Transmission Lines Not Insulated?
- Why Don’t Birds and Squirrels Get Electrocuted on Power Lines?
- Skin Effect and Factors Affecting Skin Effect in Power Lines
- Ferranti Effect in Power Lines – Causes, Advantages & Disadvantages
- Corona Effect & Discharge in Transmission Lines & Power System
- Types of Insulators used in Power Transmission and Overhead Lines
- Classification of Electric Power Distribution Network Systems
- Types of Insulators used in Power Transmission and Overhead Lines
- Classification of Electric Power Distribution Network Systems
- Electric Power System – Generation, Transmission & Distribution of Electricity
- What is the Purpose of Ground Wire in Overhead Transmission Lines?
- Why is the Grounding Wire Bare and Not Insulated?
- Why is Power Transmitted at High Voltage Instead of High Current?
- Why is the Ground Wire Always Positioned Above the Overhead Power Lines?


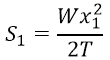

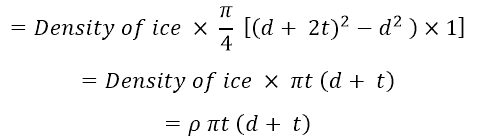
 Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet? Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs?
Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs? Is It Dangerous to Carry a Battery in an Elevator?
Is It Dangerous to Carry a Battery in an Elevator? Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System?
Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System? Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines?
Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines? Why is a Capacitor Bank Connected in Parallel and Not in Series for P.F?
Why is a Capacitor Bank Connected in Parallel and Not in Series for P.F?