What is the Difference between LDR (Photoresistor) and LED (Light Emitting Diode)?
LDR and LED are both semiconductor-based devices whose operation is associated with light. LED produces light when an electrical current pass through it while the LDR resistance decreases and allow current when light falls on it. Apart from this, they have many other differences between them.
Before going into the differences between LDR and LED, let’s look at their basics first.
LDR
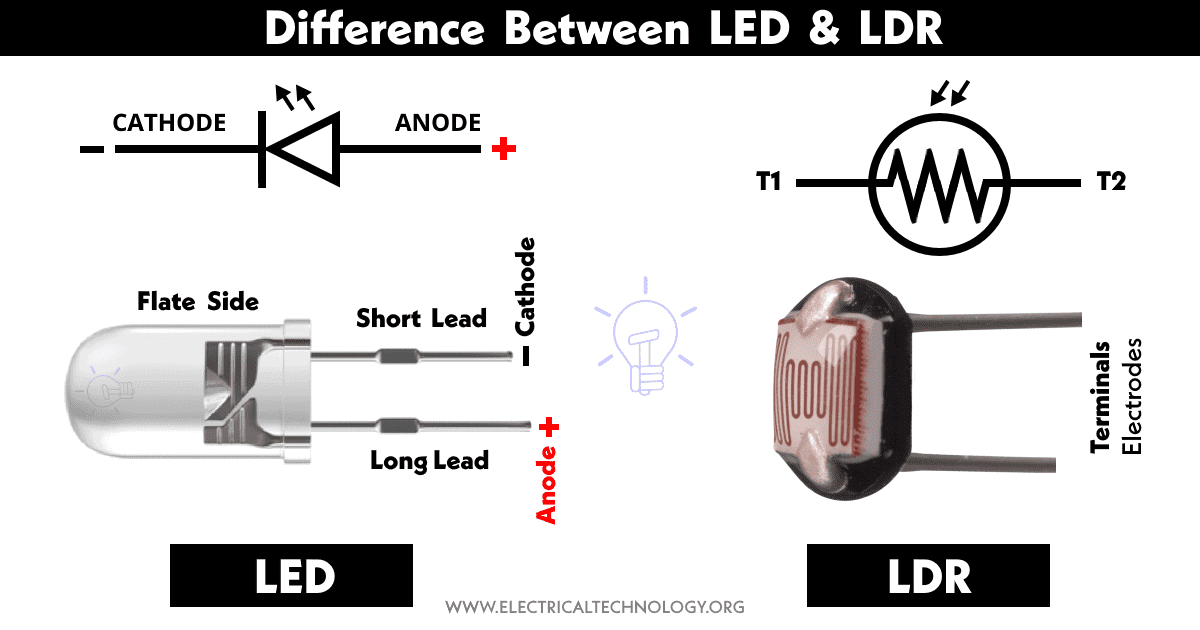
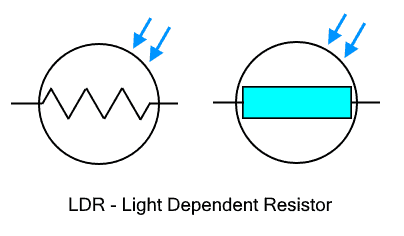
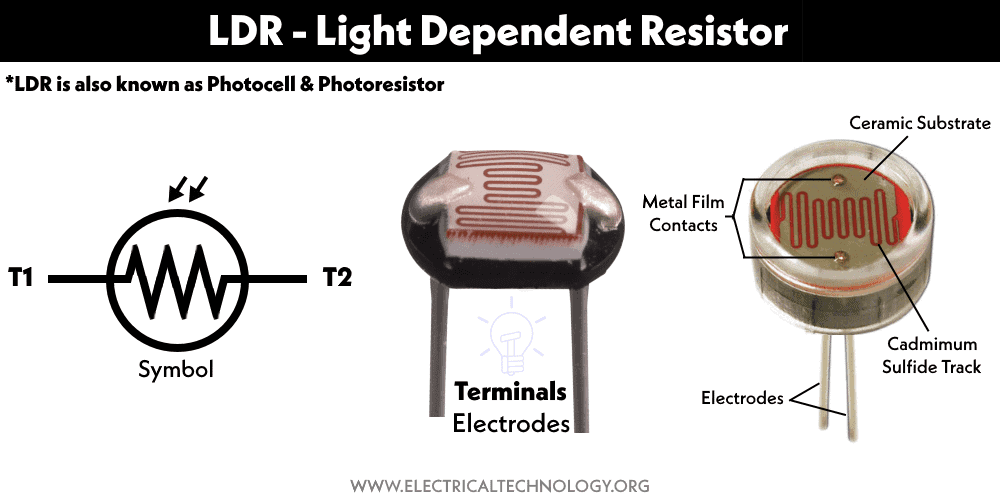
LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) also known as photocell or photoresistor is a type of light-sensitive resistor or variable resistor whose resistance decrease when exposed to light.
LDR works on the principle of photoconductivity. It is made of photoconductive semiconductor material whose resistance varies inversely with the change in light intensity. There are no or fewer electrons in darkness. When bright light shines on it, the photons in the light pass their energy to the material generating more free electrons that participate in the condition. Thus the resistance of LDR decreases.
There are different semiconductor materials having photoconductive properties. However different material shows response to different wavelengths such as visible, infrared, and ultraviolet light. The material used in the construction of LDR is N-type semiconductors such as cadmium selenide CdSe, Cadmium sulfide CdS, etc.
LDR is a symmetrical device having two same terminals. It works in both directions.
It is used in light sensing applications such as automatic street lights, solar trackers, object counters, burglar alarms, camera shutter control fire alarms, etc.
LED
The LED also known light emitting diode is a type of diode that emits light when an electric current pass through it. It converts electrical energy into light energy. The light can be infrared, visible, and ultraviolet.
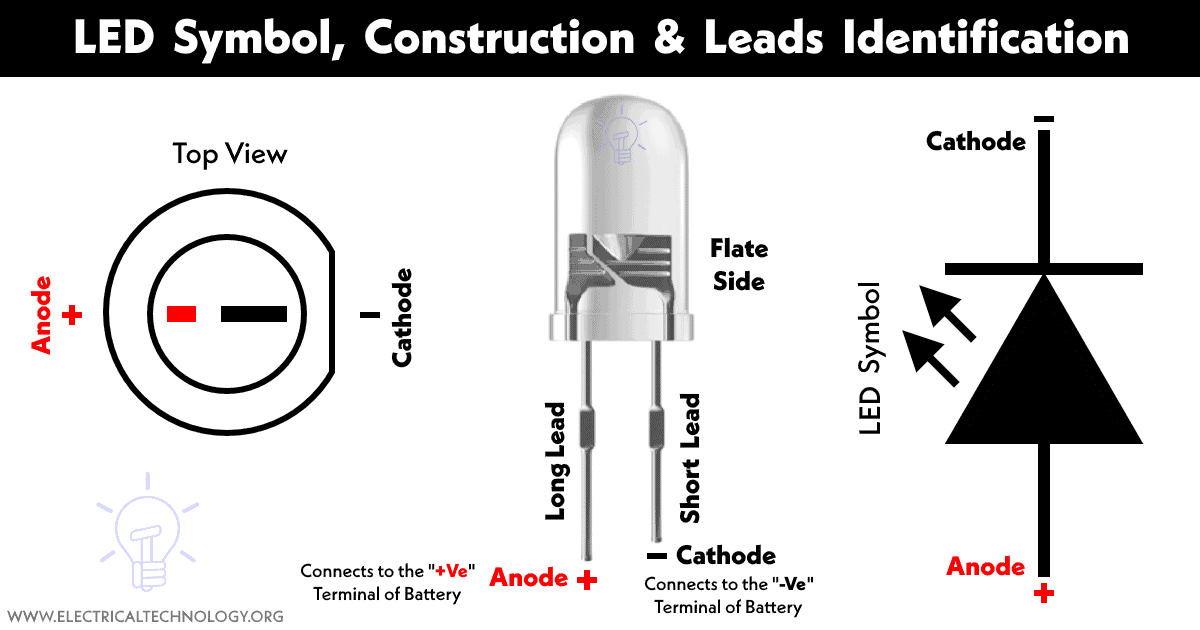
It is a PN junction diode that radiates light when connected in forward bias. The junction is converted into a transparent epoxy to prevent the junction from contamination as well as radiate light in all directions.
LED works on the principle of Electro-Luminance. According to it, a material emits light when an electric current passes through it. There are certain semiconductors that possess such properties as gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, and indium phosphide compounds. Different materials emit different color lights.
LED emits light due to electron-hole combination. Electron and hole combine and release energy equal to the band gap energy. The materials that emit light have direct band gap between conduction and valence band. It emits energy equal to the band gap in the form of photons or light. Other semiconductors such as silicon and germanium possess indirect band gaps that release energy in form of heat.
It had two terminals name anode (+) and cathode (-). It must be operated in forward bias. Reverse biasing an LED can permanently damage it.
Comparison between LDR and LED
The following table shows some of the key differences between light emitting diode (LED) and a light dependent resistor (LDR).
Related Posts:
- Difference between LED and Photodiode
- Difference between Photodiode and Photoresistor (LDR)
- Difference Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
Main Differences between LED and LDR
Definition
- LDR Light Dependent Resistor is a type of variable resistor whose resistance depends on the intensity of light
- LED light emitting diode is a type of diode that emits light when an electric current pass through it.
Function
- LDR is used for sensing light intensity to control the flow of current in current. It is a light-based switch.
- LED is used to convert electrical energy into light energy.
Structure
- LDR is made of a single layer of n-type semiconductors.
- LED is a PN junction diode made of two or more than two semiconductor layers.
Material
- LDR is made of semiconductor that is sensitive to light such as Cadmium selenide CdSe, cadmium sulfide CdS, etc.
- LED is made of semiconductor that emits light when energized such as gallium arsenide, gallium phosphide, and indium phosphide.
Working principle
- LDR works on the principle of photoconductivity. It says the material conductivity increases when exposed to light.
- LED works on the principle of Electro-Luminance. In this phenomenon, a material emits light when current pass through it
Applications
- LDR is used in light-based switching applications such as street lights that automatically switch between sunset and sunrise. Other applications such as burglar alarms, fire alarms, object counters, camera shutter control, etc.
- LED is basically used to produce light. It is used in illumination, lightning applications and digital advertisement boards and alphanumeric displays, etc.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Thermistor and Thermocouple
- Difference Between Sensor and Actuator
- Difference between Sensor and Transducer
- Difference Between Clipper and Clamper Circuit
- Difference Between Transistor and Thyristor (SCR)?
- Difference between Active and Passive Components
- Difference Between JFET and MOSFET
- Main Difference Between Clipper and Clamper Circuit
- Difference Between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET
- Difference Between BJT and FET Transistors
- Difference between RTD and Thermocouple
- Applications of Diodes

 What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground?
What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground? Difference Between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film Solar Panels
Difference Between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film Solar Panels Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode Difference Between Amplifier and Operational Amplifier
Difference Between Amplifier and Operational Amplifier