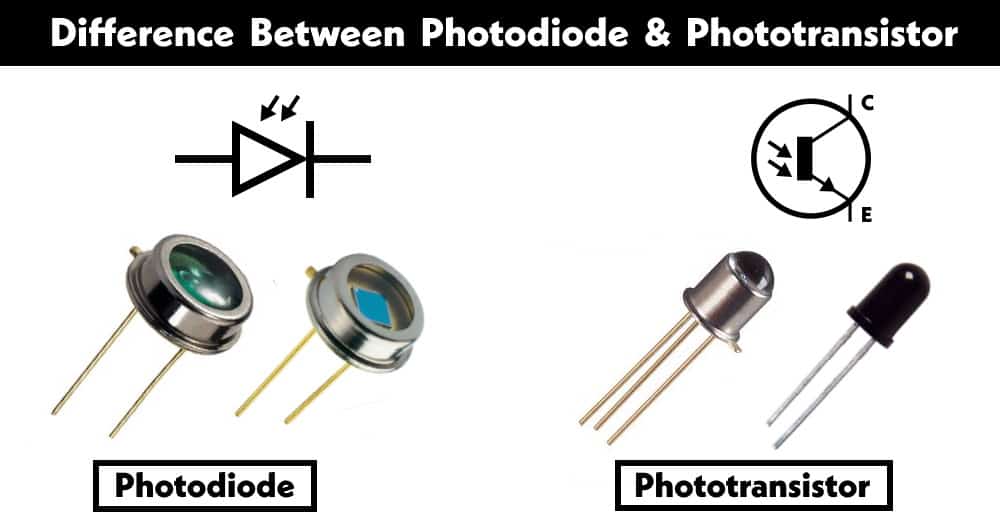
What is the Difference between Photodiode and Phototransistor?
Photodiode and phototransistor are often confused with each other for their similar operation. Both are semiconductor-based components used for sensing light intensity and converting it into electrical signal but they are quite different.
Before going into the list of differences between photodiode and phototransistor, let’s discuss their basics first.
- Related Post: Difference between LED and Photodiode?
What is a Photodiode?
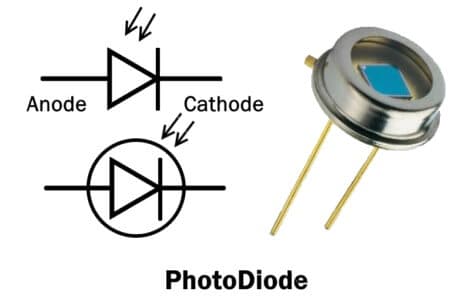
Photodiode is a light-sensitive diode that converts light energy into electrical energy. It is made of silicon or germanium. It is a single PN junction device that works on the principle of the photoelectric effect.
Photodiode has a similar construction as a normal PN junction diode except the junction is exposed to light. A lens is used to focus the light upon the junction. When the light hits the junction, it creates electron-hole pair that flows in opposite direction towards anode & cathode. As a result, a current called photoelectric current flows through the connected circuit.
A photodiode is designed to operate in reverse bias.
Features of Photodiode
- It is a light-sensitive PN junction diode.
- It converts light energy into electrical energy.
- It has two terminals; anode and cathode.
- It has a similar structure as a normal PN junction diode except for a light-sensitive exposed junction.
- It can be used in both forward and reverse bias.
- It produces both voltage and current.
- It is mainly used in solar cells to power electrical equipment from solar energy.
Related Posts:
- Photodiode – Symbol, Types, Construction, Working and Applications
- LED – Light Emitting Diode: Construction, Working, Types & Applications
What is a Phototransistor?
A phototransistor is a light-sensitive transistor that is used to amplify the photoelectric current generated from converting light energy. It is a two or three-terminal device depending on the design. It can be either a BJT (bipolar junction transistor) or FET (Field Effect Transistor) made of three layers.
It has three regions; emitter, collector, and the base region. The collector region has a large area as compared to a normal BJT. The Base region is exposed to light. The light enters the base region through the lens that also focuses the light. The photon particles hit the junction and release electron-hole pair due to the photoelectric effect. The electron-hole pair generates a base current that is amplified by the transistor.
The output or the collector current depends on the base current whose magnitude depends on the light intensity. Therefore, the collector current is directly proportional to the intensity of light hitting the transistor.
It has two PN junctions similar to a BJT transistor.
Features of Phototransistor
- It is a light-sensitive transistor that amplifies the current generated from light energy.
- It converts light energy into electrical energy and also amplifies it.
- It has two or three terminals depending on its design.
- It has a similar structure to a transistor except it has a light-sensitive base region.
- It is connected only in forward bias.
- It has a current gain that amplifies the current generated from light.
- Due to the amplification factor, it has a very high sensitivity
- It requires a power source to operate.
- It is mainly used for detecting or sensing light intensity.
Key Differences between Photodiode and Phototransistor
| Photodiode | Phototransistor |
| Photodiode is a semiconductor component that converts light energy into electrical energy. | Phototransistor is a semiconductor component that amplifies the current generated from light energy. |
| It is basically a light-sensitive PN junction diode with an opening or exposed junction for light. | It is basically a light-sensitive BJT transistor with an exposed base region. |
| It is made from 2 layers of semiconductor material | It is made from 3 layers of semiconductor material |
| It is made of a single PN junction. | It has two PN junctions to form either NPN or PNP structure. |
| It has only two terminals i.e. anode and cathode. | It has either two or three terminals depending on the design. |
| It can be configured in forward and reverse bias. | It is used in forward bias. |
| It only converts light energy into electrical current. | It also amplifies the current using an external source. |
| It has less sensitivity as compared to a phototransistor. | Due to the amplification factor, it is more sensitive. |
| It has a quick response time. | It has a relatively slower response time. |
| It does not require a power source to operate. | It requires a power source with proper biasing to operate. |
| It generates both current and voltage. | It only generates current. |
| It is cheap. | It is expensive than photodiode. |
| Photodiode is used for converting solar energy into electrical power using solar cells. | Phototransistors are used for sensing light in light sensors. |
Comparison between Photodiode & Phototransistor
Definition
- Photodiode is a semiconductor component that converts light energy into electrical energy.
- Phototransistor is a semiconductor component that amplifies the current generated from light energy.
Function
- Photodiode is used for converting light or solar energy into electrical energy.
- Phototransistor is used for sensing light.
Structure
- Photodiode is made of 2 layers of semiconductor to form PN structure.
- Phototransistor is made of 3 alternating layers of semiconductor to either form NPN or PNP structure.
Terminals
- Photodiode has only two terminals anode and cathode.
- Phototransistor has three terminals; emitter, base and collector.
Biasing
- Photodiode can be connected in forward as well as reverse bias.
- Phototransistor is only connected in forward bias.
Output
- The output of photodiode is current as well as voltage
- The output of phototransistor is only current.
Sensitivity
- Photodiodes are less sensitive as compared to phototransistors.
- Phototransistor is far more sensitive due to their amplification factor.
Response Time
- Photodiode has a very quick response time.
- Phototransistor has a relatively slower response time.
Cost
- Photodiode is cheap. It does not require an extra power source to operate. Instead, it acts as a power source.
- Phototransistor is expensive. It also requires an extra power source with proper biasing to detect light.
Applications
- Photodiode is mainly used for the conversion of solar energy into electrical energy but it is also used for sensing light in applications such as optical fiber communication, object counter, etc.
- Phototransistors are mainly used for detecting light & they find applications in printers, CD-ROM, remotes, relays, etc.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Thermistor and Thermocouple
- Difference Between Sensor and Actuator
- Difference between Sensor and Transducer
- Difference Between Clipper and Clamper Circuit
- Difference Between Transistor & Thyristor (SCR)?
- Difference between Active and Passive Components
- Difference Between JFET and MOSFET
- Main Difference Between Clipper and Clamper Circuit
- Difference Between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET
- Difference Between BJT and FET Transistors
- Difference between RTD and Thermocouple

 Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground
Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground?
What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground? Difference Between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film Solar Panels
Difference Between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film Solar Panels Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing
Difference Between Static Balancing and Dynamic Balancing Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering
Difference Between Edge Triggering and Level Triggering Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode
Difference between Zener Diode and Avalanche Diode