How a Diesel Power Plant Works? Schematic Diagram, Components, Working & Applications
What is Diesel Power Plant?
The diesel power uses a diesel engine to rotate alternators and produce electrical energy. The diesel engine is used as a prime mover and this power plant is known as a diesel power plant.
Due to the combustion of diesel, rotational energy is generated. The alternator is connected with the same shaft of the diesel engine. And the alternator is used to convert the rotational energy of the diesel engine into electrical energy.
In most cases, the diesel power plant is used to generate electrical energy for small-scale production and at the load end. When the grid power is not available, the diesel engine is used to supply load in emergency conditions.
Generally, the capacity of diesel power plants is between 2 to 50 MW is used in central power plants to meet peak demand in steam power plants and hydroelectric power plants. But nowadays, due to the high cost of fuel, diesel engines are not used for such applications.
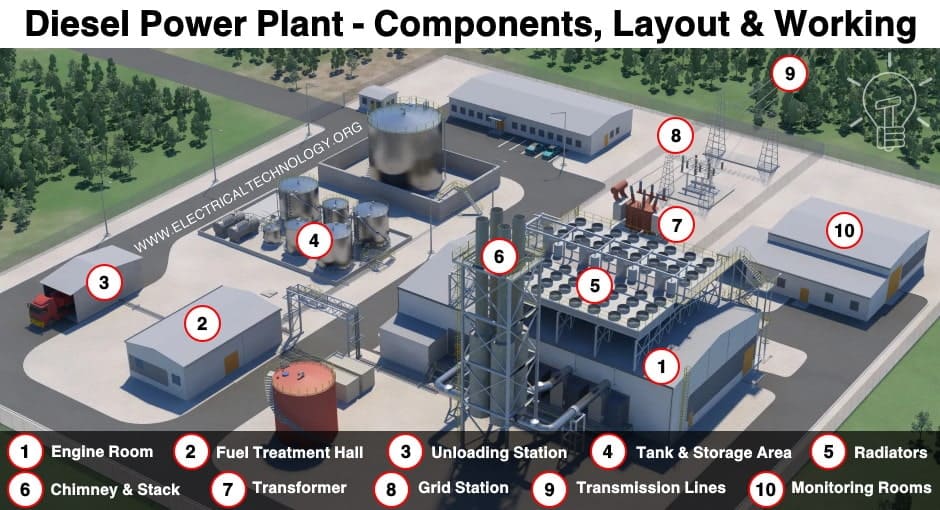
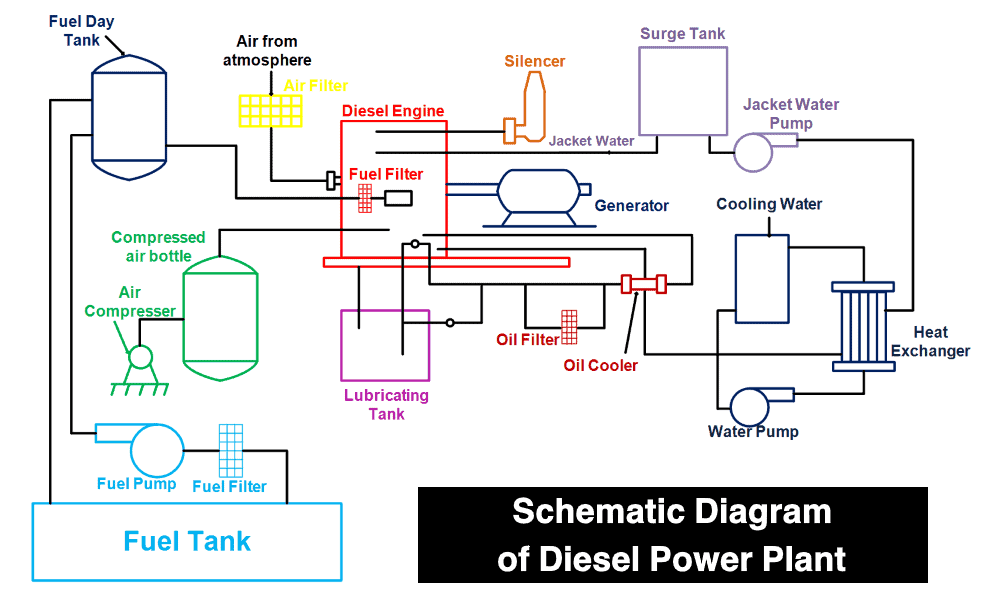
Components, Working & Schematic Diagram of Diesel Power Plant
The below figure shows a schematic diagram of a diesel power plant.
Click image to enlarge
Different components or system used in a diesel power plant is as listed below.
- Diesel engine
- Air intake system
- Exhaust system
- Cooling water system
- Fuel supply system
- Lubrication system
- Diesel engine starting system
Diesel Engine
A diesel engine is the main component of a diesel power plant. It is used to generate mechanical power in form of rotation energy with the help of the combustion of diesel. An alternator is connected to the same shaft as the diesel engine.
There are two types of diesel engines;
- Two-stroke engines
- Four-stroke engines
In two-stroke engines, every revolution of the crankshaft, one power stroke is developed. And in four-stroke engines, one power stroke is developed every two revolutions of the crankshaft.
Compared to four-stroke engines, two-stroke engines have a low weight-to-power ratio, are more compact, easy to start, and have low capital cost. But the thermodynamic efficiency of a two-stroke engine is less compared to four-stroke engines. Two-stroke engines require more cooling water and consume more lubricants.
Four-stroke engines are more preferred over two-stroke engines for the application of small-scale generation and DG sets. And for large-scale production, two-stroke engines are preferred. The required capacity of a diesel power plant can be calculated by the below equation.
Capacity of Plant = (Connected Load × Demand Factor) / (Diversity Factor)
The diesel engine power plant below 3 MW capacity is used as standby plants and 3 to 25 MW plants are used as baseload plants. Generally, in this type of plant, four-stroke engines are used. The plants used for baseload plants have a capacity of above 10 MW capacity and for these plants, two strokes engines are used.
- Related Post: Why Power Plant Rated in MW and Not in kVA?
Air Intake System
Large diesel engine power plant requires air in the range of 4-8 m3/kWh. In natural air, lots of dust particles are available which may damage the cylinders of engines. Therefore, air filters are used in the air intake systems.
The air filters are made of cloth, wood, or felt. In some cases, oil bath filters are used. In oil bath filters, the dust particles are oil-coated. The design of an air intake system is done in such a way that it causes minimum pressure loss during airflow.
If the pressure losses are high, it may increase fuel consumption and reduce engine capacity. To avoid clogging, the air filters must be cleaned periodically. In a large capacity power plant, a silencer is used between the engine and intake system to reduce noise pollution.
Exhaust System
While combustion of diesel, gases are produced. The system that is used to remove these gases is known as an exhaust system. The exhaust system aims to discharge gases from the engine into the atmosphere.
The exhaust systems are designed in such a way that they will remove gases without losing pressure. If pressure releases, it requires more work to do to exhaust gases. And it will increase fuel consumption and reduce the power output of diesel engines.
To reduce the noise level, the exhaust system must be provided with mufflers and silencers. With the help of flexible exhaust pipes, the vibration must isolate from the plant.
The exhaust system is needed to cover by asbestos to avoid heat transfer and it must be cleaned periodically.
Cooling Water System
The IC engine works by burning fuel with air and the percentage utilization of energy is as below;
- 30-37% – useful work
- 30-35% – carried by exhaust gases
- 0-12% – lost by radiation, convection, and conduction
- 22-30% – heat energy flows from gases to cylinder walls
Therefore, in an IC engine, 22-30% of energy is lost in form of heat energy. And to avoid overheating of the engine, it requires a cooling system. There are two types of cooling systems;
- Direct cooling
- Indirect cooling
Direct cooling is also known as air cooling and indirect cooling is also known as water cooling. Generally, air cooling is used for small-capacity engines. And it uses cooling fins and baffles to remove heat from the engine. A water-cooling system is used for large and medium capacity engines. The water-cooling system is used a water jacket, radiator, and piping connections.
Fuel Supply System
In a diesel power plant, as the name suggests, diesel is used as a fuel. The fuel supply system has to perform the below functions.
- Depending upon the capacity of the engine and supply hours, the storage tank is required to store the diesel.
- Before supplying fuel to the engine, the fuel must be filtered and it does not contain any impurities.
- Metering of fuel is necessary.
- According to the load in each cycle, it must inject the exact quantity of fuel.
- Provide return path to unused fuel.
- In a multi-cylinder engine, it is required atomization of fuel and even distribution of fuel to each cylinder.
There are three types of mechanical fuel injection systems;
- Common rail system
- Individual pump system
- Distributor system
Lubrication System
In the IC engine, the piston-cylinder arrangement is referred to a very large variation of temperature. It works at a maximum temperature of around 2000˚ C or higher than this. At such a high temperature, the lubricating material may convert into gummy material. And it results in sticking piston rings.
The engines run on high load conditions and cause friction loss in case if the lubrication system fails. Therefore, the lubrication system is necessary for the IC engine and it requires an adequate quantity of oil reach to all parts of the engine.
The lubrication system prevents direct contact between two metals and will reduce the wear and tear in moving parts. The below-listed components of the IC engine must be lubricated;
- Piston and cylinder
- Main crankshaft bearings
- Cam, camshaft, and its bearings
- Ends of bearings at connecting rod
There are three types of lubricating systems;
- Mist or charge lubricating system
- Wet sump injection system
- Dry sump injection system
Related Post: Thermal Power Plant – Components, Working and Site Selection
Diesel Engine Starting System
At the time of starting, the temperature and pressure of the cylinder are not sufficient to initiate the combustion. Hence, starting of the engine is not conductive for initiation of combustion. There are several methods introduced to start a diesel engine. Some of these methods are listed below.
- Hand or kick-starting
- Electrical starting
- Compressed air
- Auxiliary petrol engine
- Hot bulb ignition
- Special cartridge starting
Form these methods, the electrical starting method is the most popular method to start a diesel engine. In this method, a battery is used with a series-wound motor (starting motor). This arrangement is designed to operate on a large current at low voltage. The starting motor is connected with the engine flywheel through gears and supplies torque till the engine starts.
Site Selection of Diesel Power Plant
The factors affecting a selection of a location for diesel power plant are listed below.
- Bearing capacity: The diesel engine is placed on a foundation. If the bearing capacity of selected land is high then it does not require high depth for a foundation. And it will save the initial cost of a power plant.
- Transportation facility: The plant requires heavy pieces of machinery. Hence, the selected site must have an adequate transportation facility.
- Labor: Large capacity diesel power plant requires several labors.
- Availability of water: The diesel power plant requires water for cooling purposes.
- Future expansion: There is some extra land available for future expansion.
- Availability of fuel: This plant requires a high volume of fuel (diesel). So, a site should be selected where fuel is available easily.
- Distance from the populated area: The operation of a diesel engine pollutes nearby areas. Hence, the plant must be located at a far distance from the human being.
- Distance from load center: To avoid transmission loss, the site should be selected near the load center.
- Related Post: What is Nuclear Power and How Nuclear Power Plant Works?
Advantages & Disadvantages of Diesel Power Plants
Advantages
The advantages of diesel power plants are listed below.
- It can start and stop quickly when required.
- This plant can be located at any place and it is easy to install for a small capacity power plant.
- It does not require more space.
- For varying loads, this plant responds quickly.
- The water is required only for cooling purposes. So, a very little quantity of water is required.
- The thermal efficiency of this plant is higher than a steam power plant.
- The diesel power plant can be efficiently used up to 100 MW.
- Less manpower is required.
- It can burn a wide range of fuel.
- Fewer fire chances.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of diesel power plants are listed below.
- The generation cost per unit is very high. As the operation of this plant depends on the price of diesel. And diesel prices are high.
- The capacity of a diesel power plant is less compared to a steam power plant and hydroelectric power plant.
- It creates noise pollution and carbon pollution by the combustion of diesel.
- It requires high maintenance and lubrication costs.
- This plant is not capable to meet continuous overload demand.
- The life of this plant is less compared to other power plants.
Related Posts:
- What is HVDC? High Voltage Direct Current Power Transmission
- Differences Between HVAC and HVDC Power Transmission
- Advantages of HVDC over HVAC Power Transmission
Application of Diesel Power Plants
The applications of diesel power plants are as follows;
1) Installation of plant
The plant can be easily installed in a power system network. But if you consider economic consideration, the capacity of pant limits up to 5 MW to 50 MW. These limits also depend on the load capacity, availability of fuel, water, and space.
2) Peak load plant
The diesel power plant is used with thermal power plant and hydroelectric power plant to meet peak demand. It reduces the per-unit cost of power generation. It can easily start and stop with demand and varying with load variation.
3) Emergency plant
The diesel engine can be used as an emergency plant. When the power of the grid is not available, the diesel engine is used as a backup plant for emergency conditions.
4) Mobile plant
The small and medium capacity of the diesel power plant can be fixed on a truck or trailer. This plant can be used as a mobile power plant and we can take this plant to supply where grid power is not available. This plant is also used as an emergency plant while power failure.
5) Stand by unit
This plant can be used as a stand-by unit with a hydroelectric power plant. When the water is not available sufficiently in the hydro power plant, to meet power demand the diesel power plant operates parallel with the hydropower plant.
6) Power plant for small industries
This plant can be used to run a small industry for short periods where the reliability of power is essential throughout the day.
7) Nursery station
In some areas where a grid is not available or any developing area where does not have enough load to connect with a grid, the diesel power plant is used as a temporary solution to supply power. And remove when the grid is connected.
Related Posts:
- What is Electricity? Types, Sources & Generation of Electricity
- What is Electrical Power? Types of Electric Power and their Units
- Energy and Power Consumption Calculator – kWh Calculator
- FACTS – Flexible AC Transmission System – Types of FACTS Controllers & Devices
- Why Electric Power Transmission is Multiple of 11 i.e. 11kV, 22kV, 66kV etc?
- Corona Effect & Discharge in Transmission Lines & Power System
- Why Power Transmission Cables & Lines are Loose on Electric Poles & Transmission Towers?
- Difference between AC and DC Transmission System & Power Lines
- Design and Installation of EHV/EHV and EHV/HV Substations
 Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines?
Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines? Why is a Capacitor Bank Connected in Parallel and Not in Series for P.F?
Why is a Capacitor Bank Connected in Parallel and Not in Series for P.F? Why Does Japan Use Both 50Hz and 60Hz in Its Power System?
Why Does Japan Use Both 50Hz and 60Hz in Its Power System? Why is the Neutral Wire Size Smaller than the Phase Wire?
Why is the Neutral Wire Size Smaller than the Phase Wire? Why is the Ground Wire Size Smaller than the Hot Wire?
Why is the Ground Wire Size Smaller than the Hot Wire? Why Must Neutral and Ground Wires Be Bonded in the Main Panel?
Why Must Neutral and Ground Wires Be Bonded in the Main Panel?