Main Difference Between Depletion MOSFET and Enhancement MOSFET
MOSFET
MOSFET is an acronym for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. It is a type of FET (Field Effect Transistor) that has an insulated metal oxide layer between its gate and channel. On the contrary, JFETs gate is connected with its channel. The plus point of the insulated gate is its superior speed and performance with very little leakage current.
Now MOSFET is classified into two types depletion type MOSFET “D-MOSFET” and Enhancement type MOSFET “E-MOSFET. Both of these MOSFET’s are widely used in electronics, integrated and embedded circuits.
The MOSFET has 4 terminals Drain, Gate, Source and Body. However, the body terminal is always connected with the source terminal. Therefore, we are left with only three terminals. The MOSFET conducts current between the source and drain. The path for current between the source and drain is called a channel. The width of this channel is controlled by the voltage at the gate terminal.
Related Posts:
Before going into the differences between D-MOSFET & E-MOSFET, we are going to little bit discuss their basics first.
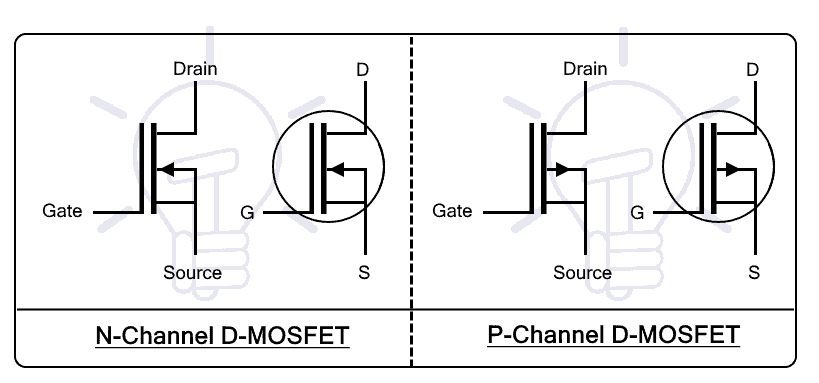
D-MOSFET “Depletion MOSFET”
Depletion MOSFET or D-MOSFET is a type of MOSFET where the channel is constructed during the process of manufacturing. Therefore, the D-MOSFET can conduct between its drain and gate when the VGS = 0 volts. Therefore, D-MOSFET is also known as normally ON transistor.
 If Gate and source is connected in forward bias and the VGS is increased, more majority carriers will get induced in the channel and its width will increase. It will result in increasing the current flow between drain and source.
If Gate and source is connected in forward bias and the VGS is increased, more majority carriers will get induced in the channel and its width will increase. It will result in increasing the current flow between drain and source.
If the gate is connected in reverse bias and voltage is decreased beyond 0v, the channel width will decrease as well as the current will decrease. Decreasing the channel width will deplete the channel of the charge carriers until the channel width becomes zero and it vanishes. At this point, the D-MOSFET stops conduction and this VGS voltage is called VTh threshold voltage.
 The D-MOSFET can be N-channel D-MOSFET or P-channel D-MOSFET depending on the channel being used. The type of channel also affects its biasing as well as its speed and current capacities.
The D-MOSFET can be N-channel D-MOSFET or P-channel D-MOSFET depending on the channel being used. The type of channel also affects its biasing as well as its speed and current capacities.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Diode and SCR (Thyristor)
- What is The Difference Between Transistor and Thyristor (SCR)?
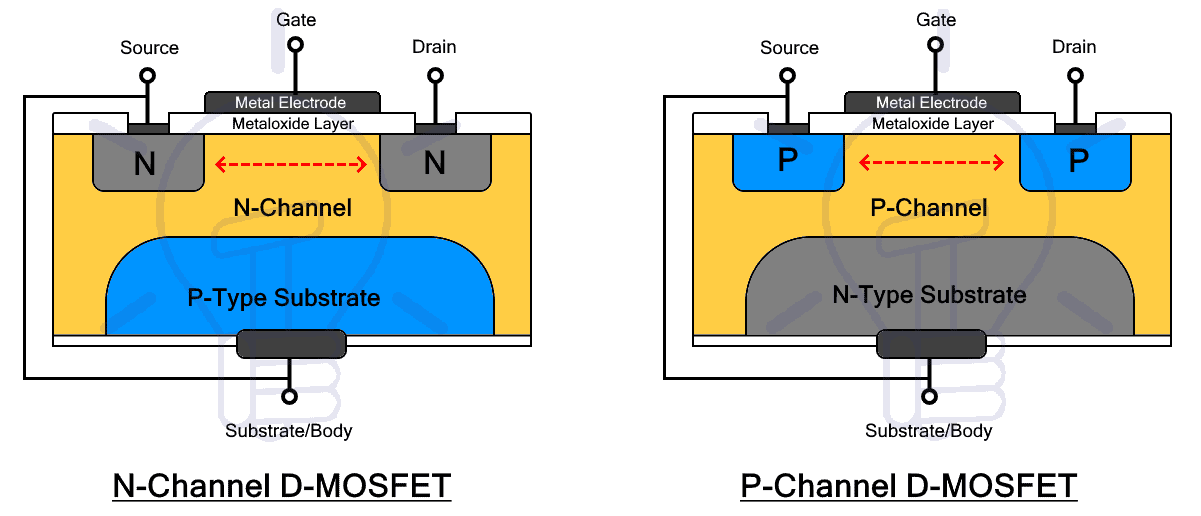
In N-channel D-MOSFET, the source, drain and channel are made during the manufacturing from N-type material upon a P-substrate. The channel contains electrons as charge carriers. There is a metal oxide insulating layer between the gate electrode and the channel or P-substrate.
 When the gate is connected in reverse bias i.e. negative voltage is applied, the holes from the P-substrate will attract towards the gate depleting it of the electrons and reduce the channel size. At a certain –Vth, the MOSFET will stop conduction. Therefore, N-channel D-MOSFET has a negative threshold voltage
When the gate is connected in reverse bias i.e. negative voltage is applied, the holes from the P-substrate will attract towards the gate depleting it of the electrons and reduce the channel size. At a certain –Vth, the MOSFET will stop conduction. Therefore, N-channel D-MOSFET has a negative threshold voltage
In P-channel D-MOSFET, The source, drain, and channel is made up of P-type material upon an N-type substrate. P-channel has holes as the charge carrier. Therefore, to reduce the channel width or to attract electrons from the N-substrate, P-channel MOSFET is applied with positive gate voltage VGS. This positive voltage attracts the electrons from the substrate to deplete the channel of holes, thus eliminating the channel as well as the current flow. Therefore, the P-channel D-MOSFET has a positive threshold voltage.
If the gate and source is connected in forward bias, the potential difference will induce more charge carriers inside the channel thus enhancing (increasing the width) of the channel.
The D-MOSFET can work in both depletion and enhancement modes. While the enhancement MOSFET cannot work in depletion mode.
Related Posts:
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) | Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Thyristor and Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) – Thyristors Applications
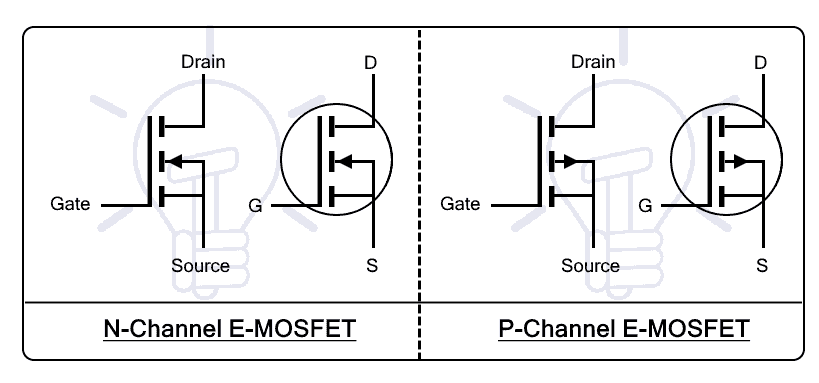
E-MOSFET “Enhancement MOSFET”
Enhancement MOSFET or E-MOSFET is a type of MOSFET where there is no channel constructed during its fabrication but it is induced in the substrate using the gate voltage. The E-MOSFET does not conduct when there is no gate voltage i.e. VGS= 0v. Therefore, E-MOSFET is also known as normally OFF transistor.
 In case, the VGS or gate voltage is zero, there is no channel. Therefore, there is no path for the conduction of current between its source and drain.
In case, the VGS or gate voltage is zero, there is no channel. Therefore, there is no path for the conduction of current between its source and drain.
 By applying a voltage to the gate, charge carriers are induced in the substrate that produces a channel for the conduction of current between the source and drain.
By applying a voltage to the gate, charge carriers are induced in the substrate that produces a channel for the conduction of current between the source and drain.
 E-MOSFET is also classified into N-channel and P-channel E-MOSFET. The biasing and electrical characteristics of both channels are quite different.
E-MOSFET is also classified into N-channel and P-channel E-MOSFET. The biasing and electrical characteristics of both channels are quite different.
N-channel and P-channel MOSFET has the same operation as the Depletion type MOSFET except there is no channel, to begin with; instead, the gate voltage is used to inject the charge carriers in the substrate to induce a channel between the source and drain. The gate is connected in forward bias to induce the charge carriers in the channel. Once the channel is induced, the current starts to flow between the source and drain.
Related Posts:
Differences between Depletion MOSFET and Enhancement MOSFET
The following comparison table shows the main differences between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET.
| Depletion MOSFET | Enhancement MOSFET |
| The type of MOSFET where the channel depletes with the gate voltage is know as depletion or simply D-MOSFET. | The type of the MOSFET where the channel is enhanced or induced using the gate voltage is known as E-MOSFET. |
| The channel is fabricated during manufacturing. | There is no channel during its manufacturing. |
| It conducts current between its source and drains when there is no Gate voltage VGS. | It does not conduct current when there is no Gate voltage VGS. |
| Applying reverse voltage to the gate reduces the channel width. | Applying reverse voltage does not affect E-MOSFET since there is no channel. |
| Applying forward voltage to the gate increases the channel width. | Applying the forward voltage generates and increases the width of the channel. |
| It can work in both depletion and enhancement mode. | It can only work in enhancement mode. |
| It is a normally ON transistor. | It is a normally OFF transistor. |
| It switches OFF with reverse biasing of gate. | It switches ON with the forward biasing of the gate. |
| There is no threshold voltage for switching ON the MOSFET. | There a threshold voltage at which the MOSFET switches ON. |
| Diffusion or subthreshold current does not exist. | E-MOSFET has sub-threshold current leakage between its source and drain. |
That’s it. Now you know the basic difference between the D-MOSFET and E-MOSFET and all its related components and types. Let us know in the comment box if you have any other differences between them.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- Difference Between 8085 and 8086 Microprocessor – Comparison
- Difference Between CPU and GPU – Comparison
- Difference between Analog and Digital Circuit – Digital vs Analog
- Difference between Electron Current and Conventional Current
- Difference Between RAM and ROM – Comparison
- Difference Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmission
- Difference between Inverter and UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply
- Difference Between Online UPS and Offline UPS – Which One is Better?
- Diode Symbols – Electronic and Electrical Symbols
- Transistor, MOSFET and IGFET Symbols
- How to Check a Transistor by Multimeter (DMM+AVO) – NPN and PNP – 4 Ways
- How to Test a Diode using Digital and Analog Multimeter – 4 Ways.

 Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet? Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs?
Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs? Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground
Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground Is It Dangerous to Carry a Battery in an Elevator?
Is It Dangerous to Carry a Battery in an Elevator? What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground?
What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground? Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System?
Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System?