Shockley, Zenner & Diode Rectifier Formulas and Equations
Diode Equation for I-V Curve
The I-V curve (diode characteristic curve) can be find by the following no linear equations. This equation is also known as Ideal Equation of Diode or Diode Law.
i = IS ( eqv/kT – 1 )
Where:
- i = Current flowing through the diode
- Is = Reverse or dark saturation current (Typical value for silicon is 10-12 Amperes)
- e = Base of the neutral logarithm (2.71828)
- q = Charge on electron (1.602 x 10-19) in coulombs (Absolute Value of electron charge).
- v = Applied voltage across the diode
- k = Boltzmann’s constant (1.380 x 10-23 jouals/Kelvin)
- T = Absolute Temperature in Kelvin (Typical Room Temp is 300 Kelvin)
Shockley Diode Equation:
Where
- ID = current through the diode
- VD = diode voltage
- Is = leakage or reverse saturation current
- n = emission coefficient or ideality factor, for germanium n=1, for silicon it ranges in 1.1-1.8.
- VT = thermal voltage which is
Where
- q = charge of electron = 1.6022 x 10-19 coulomb
- T = absolute temperature in Kelvin (K = 273 + °C)
- k = Boltzmann’s constant = 1.3806 x 1023 J/K
Zenner Diode Formulas & Equations
You may check the Zener diode based regulator calculator in the previous post.
Series Current
IS = VIN – VZ/RS ….. (Ohm’s Law)
Zener Current
IZ = IS – IL
Load Current
IL = VL/RL
Load Voltage
VL = VZ
Change in Load Voltage
∆VL = IZ RZ
Output (Regulated) Voltage
- VOut = VIN – I R
- VOut = VIN – (IZ + IL)/RS
- VOut = (VIN – IS)/RS
Series Resistance
RS = (VL – Vout) / (IZ + IL) = (VL – Vout)/(IS)
Max Series Resistance
RS (MAX) = RL (MIN) x [(VIN (MIN) / VZ) -1]
RS (MAX) = RL (MIN) x [(VIN (MIN) – VZ)/IL(MAX)]
Value of Resistor
R = [(VIN (MIN) – VOUT)/(IL + 10)]
Power of Resistor
RP = (VIN (Max) – Vout) 2 / R
Power of Zener Diode
ZP = (VIN(MIN) – VOUT) / R) x VOUT
Output Ripple
VR (OUT) ≈ VR (IN) x (RZ/RS)
Diode Rectifier Equations:
A rectifier’s output contains DC as well as AC components, So;
Output DC Power:
Pdc = Vdc Idc
Where
- Vdc is the average output voltage
- Idc is the average output current
Output AC Power:
Pac = Vrms Irms
Where
- Vrms Is the rms of output voltage
- Irms is the rms of output current
Rectifier Efficiency:
The efficiency of the rectifier denote by η is given by:
Where
- Pdc is the output DC power
- Pac is the output AC power
Output AC Voltage:
The rms of AC component of the output voltage is:
Form Factor:
The ratio of RMS voltage to the average dc voltage,
Ripple Factor:
It’s the ratio between the AC and DC component of the rectifier. It shows the purity of the DC output.
Related Formulas and Equations Posts:
- Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and Equations
- Resistance, Conductance, Impedance and Admittance Formulas
- Resistance, Capacitance & Inductance in Series-Parallel – Equation & Formulas
- Equations & Formulas For RLC Circuits (Series & Parallel)
- Basic Electrical Quantities Formulas
- Power Formulas in DC and AC Single-Phase & Three-Phase Circuits
- Magnetic Terms used in Magnetic Circuits – Definition & Formulas
- Formula and Equations For Inductor and Inductance
- Formula and Equations For Capacitor and Capacitance
- Electric & Magnetic Flux, Density & Field Intensity Formulas
- Formula & Equations for Ohm’s, Kirchhoff’s & Coulomb’s Laws
- Voltage & Current Divider Rules (VDR & CDR) Equations
- Losses in Electrical Machines – Formulas and Equations
- DC Generator Formulas and Equations
- Power, Voltage and EMF Equation of a DC Motor – Formulas
- Synchronous Generator and Alternator Formulas & Equations
- Synchronous, Stepper and AC Motors Formulas and Equations
- Induction Motor & Linear Induction Motors Formulas & Equations
- Transformer Formulas and Equations
- Electrical & Electronics Engineering Formulas & Equations
- Electrical & Electronics Elements & Symbols


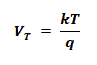

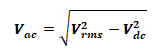

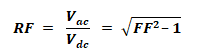
 What is the Right Wire Size for a 30A Breaker and Outlet?
What is the Right Wire Size for a 30A Breaker and Outlet? What is the Correct Wire Size for 25A Breaker and Load?
What is the Correct Wire Size for 25A Breaker and Load? What is the Suitable Wire Size for 20A Breaker and Outlet?
What is the Suitable Wire Size for 20A Breaker and Outlet? What is the Right Wire Size for 15A Breaker and Outlet?
What is the Right Wire Size for 15A Breaker and Outlet? How to Install NEMA 14-50R, 50 Amp Heavy Duty EV Outlets?
How to Install NEMA 14-50R, 50 Amp Heavy Duty EV Outlets? Why Do Doorbells Use Low Voltage of 12V-24V AC Instead of DC?
Why Do Doorbells Use Low Voltage of 12V-24V AC Instead of DC?