Coulomb’s Laws of Electrostatics
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb discovered the Laws of Electrostatics in 1785 known as Coulomb’s Law. Until 1784, no one knew about the unit of the electric charge, then the Coulomb introduced these laws after multiple experiments on force between two masses based on the Inverse Square Law. Coulomb’s laws of electrostatic can be stated as follow:
First Law
Coulomb’s first law states that like charges of electricity repel each other, whereas unlike charges attract each other.
Second Law
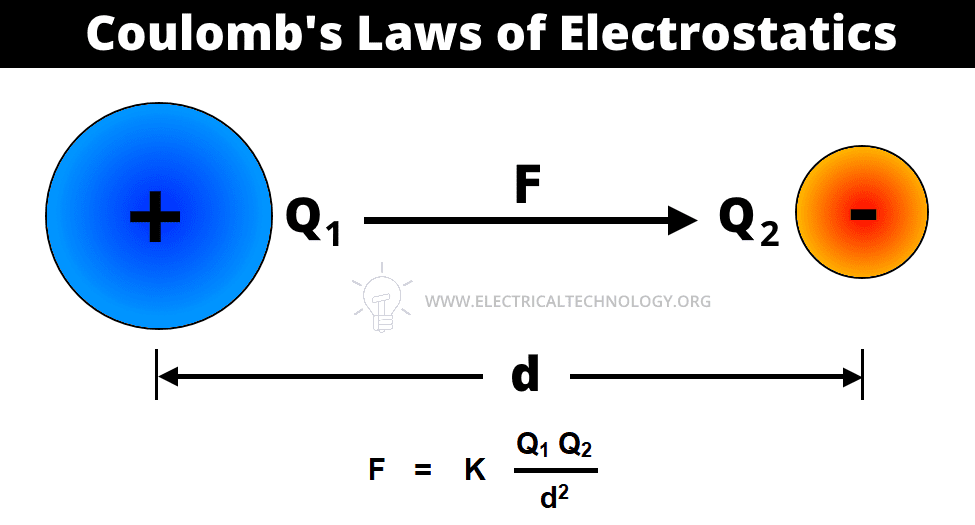
The second law of electrostatic states that the force exerted between two small charged bodies (point charges) is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In other words, the electric force of attraction or repulsion between two charged points varies directly as the product of the charged points and inversely as the square of the distance between those charge points.
Coulomb’s Laws of electrostatic can be mathematically represented as follows.
Where:
- F = Force
- Q1, Q2 = Two charged bodies or points
- d = Distance between the two charged bodies
- K = Constant which values depends on the measurement units of F, Q1 and Q2 and characteristics of the dielectric insulating medium between two charged bodies. The constant K is also represented by the symbol of λ (Lambda). The value of constant K = 1 / 4πεoεr in both SI and MKS systems.
Related Post:
- Coulomb’s Laws of Magnetic Force – Solved Example
- Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
- Lenz’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Coulomb’s Laws of Electrostatics in Vacuum & Free Space
If the medium between two charged points is vacuum or free space and the units of measurements are in MKS system (Force (F) in Newtons, Distance (d) in meters and charged body (Q) in Coulombs), then the Coulomb’s force in free space due to absolute permittivity (εo) of space would be as follows:
Where:
εo = Absolute permittivity in space
Coulomb’s Laws of Electrostatics in a Medium
If the medium between two charged bodies is an insulation or dielectric material, then the electrostatic force of repulsion or attraction between them is less than the electrostatic force in free space due to the relative permittivity (εr) of dielectric material. In that case, the coulomb’s force for such a medium is as follow:
Where:
εr = Relative permittivity of dielectric material
While the value of εo is 8.854×10-12 F/m and the value of εr in air is 1.006. If the values of Q1 and Q2 are in Coulombs, distance in meters and ε in farads per meter (F/m), then the value of force (F) is in Newtons. This way, the Coulomb’s law can be written as follow:
In short, we have added the value of K which is 1 / 4πεoεrin the first and second laws.
In case of air:
εr = 1
εo = 8.854×10-12 F/m
Q1 = Q2 = 1 Coulomb
d = 1 meter
F = 8.997 x 109 N
F = 9 x 109 N (approx.)
Hence, Coulomb’s laws of electrostatic can be written for air, vacuum and medium as follows.
Coulomb’s Law in Air Vacuum
F = 9 x 109 (Q1Q2/d2)
Coulomb’s Law in a medium
F = 9 x 109 (Q1Q2/εr d2)
According to the above explanation, One coulomb charge can be defined as follow:
When a charge (amount of electricity) is placed in air to the another uniform or non-uniform charge separated by the distance of one meter, then the force of repulsion or attraction is 9 x 109 Newton between them.
Example on Coulomb’s Laws of Electrostatic
Example:
Calculate the electrostatic force of repulsion between two alpha “α” – particles when at a distance of 10-13 meter from each other. Charge of an alpha “α” particle is 3.2 x 10-19 C. If the mass of each particle is 6.68 x 10-27 kg, compare this force with the gravitational force between them. Take the gravitational constant as equal to the 6.67 x 10-11 N-m2 / kg2.
Solution:
Here, Q1 = Q2 = 3.2 x 10-19
d = 10-13 m
Putting the values
= 9.2 x 10-2 N
The force of gravitational attraction between two particles is given by
Putting the values
= 2.976 ×10-37 N
As seen, this force is negligible as compared to the electrostatic force between these two bodies.
Good to Know:
- Permittivity (ε): The capacity of concentrating the electric flux in a dielectric or insulator is called permittivity. It is also known as dielectric constant and represented by the symbol of Epsilon “ε“.
ε = εo εr
For example, the permittivity for mica is 8.854 x10-12 x 5 = 44.27 x10-12 F/m (where εo for mica is 8.854 x10-12 and εr is 5.)
- Absolute Permittivity (εo): The ratio of D/E for an electric field in a vacuum in farad per meter (F/m) is called the permittivity of free space or the electric space constant . Where “E” is Electric Field Strength and “D” is the Resulting Flux Density.
εo = D/E = εo εr
- Relative Permittivity (εr): It is the ratio of the absolute permittivity “ε” of a material to the absolute permittivity “εo“.
εr = ε / εo
The value of εr in space and air is unity (1) i.e. εr = 1. There is no unit for relative permittivity as it is a ratio between permittivity and absolute permittivity.
- Coulomb’s Law or laws of electrostatic is related to the static electricity and capacitors (static charge).
- Coulomb’s Law or magnetic force is related to magnetism and electromagnetism (i.e. inductors, coils, solenoid etc.)
- Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction is related to static and dynamic induced EMF, magnetism and generation of electricity in alternator.
Related Posts
- Kirchhoff’s Current & Voltage Law (KCL & KVL) | Solved Example
- Ohm’s Law with Simple Explanation
- Formula & Equations for Ohm’s, Kirchhoff’s & Coulomb’s Laws
- Norton’s Theorem. Easy Step by Step Procedure with Example
- Thevenin’s Theorem. Step by Step Procedure with Solved Example
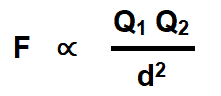

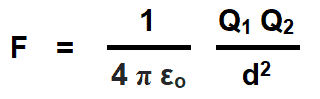


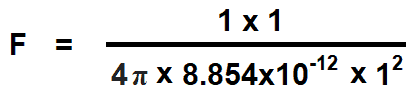

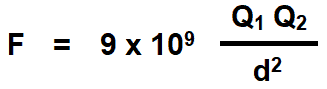
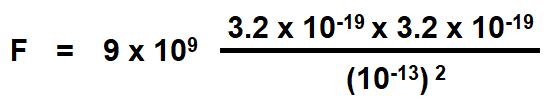
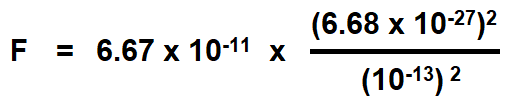
 Why is the Long Prong Neutral Instead of the Narrow Prong?
Why is the Long Prong Neutral Instead of the Narrow Prong? Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet? Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs?
Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs? Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines?
Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines? Why is a Capacitor Bank Connected in Parallel and Not in Series for P.F?
Why is a Capacitor Bank Connected in Parallel and Not in Series for P.F? Why Do Americans Use Gas Kettles Instead of Electric Kettles?
Why Do Americans Use Gas Kettles Instead of Electric Kettles?