AC Machine Formulas & Equations for Stepper and Synchronous Motors
Following are the useful equations and AC motors formulas while designing and analyzing synchronous motors, stepper motors and other related AC machines.
Synchronous Machine:
Speed of Synchronous Machine:
Synchronous machine are designed to be operated at synchronous speed, which is given by:
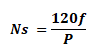
Where
- Ns is the synchronous speed
- f is the line voltage frequency
- P is the number of poles in a machine
Synchronous Motor:
Voltage Equation of Synchronous Motor:
V = Eb + Ia(Ra + jXs)
Where
- V = voltage applied
- Eb = Back emf
- Ia = Armature current
- Ra = Armature resistance
- Xs = synchronous reactance
Resultant Voltage:
The difference between the voltage applied V and back EMF is known as resultant voltage ER
ER = V – Eb
ER = Ia(Ra + jXs)
Internal Angle:
It is the angle by which the armature current Ia lags behind the resultant voltage in armature ER, and it is given by;

Back EMF Generated:
Eb = KaφaNs
Where
- Ka = constant of the armature winding
- φa = magnetic Flux per pole of the rotor
- Ns = synchronous speed of the rotor
Related Posts:
- Single-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Three-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
Different Excitations:
- Eb = V Normal Excitation Lagging Power Factor
- Eb < V Under-Excitation Lagging Power Factor
- Eb > V Over- Excitation Leading Power Factor
Input Power:
The input power of synchronous motor is given by:

Where
Φ is the angle between V and Ia
Mechanical Power In Rotor:
- α is the load angle between Eb & V
- Φ is the angle between V & Ia
- Tg is gross torque produced
- Ns is the synchronous speed
Related Posts:
- Servo Motor – Types, Construction, Working, Controlling & Applications
- Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) – Construction, Working & Applications
Stepper Motors Formulas
Step Angle:
- β = step angle, the angle of rotation of the shaft with each pulse.
- Ns = number of stator poles or teeth
- Nr = number of rotor poles or teeth
Resolution Of Stepper Motor:
The number of steps required to complete one revolution, its given by;

The higher the resolution, the higher the accuracy of the stepper motor.
Motor Speed:
Where
- n = motor speed in revolution per second
- f = stepping pulse frequency
Related Formulas and Equations Posts:
- Induction Motor & Linear Induction Motors Formulas & Equations
- Transformer Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Quantities Formulas
- Power Formulas in DC and AC Single-Phase & Three-Phase Circuits
- Electrical & Electronics Engineering Formulas & Equations
- Electric Motors Symbols


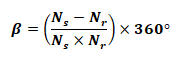

 Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground
Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground?
What is the Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground? Should You Connect GND and 0VDC? Combined AC & DC Grounding
Should You Connect GND and 0VDC? Combined AC & DC Grounding Can you Combine AC and DC Ground in a Solar Installation?
Can you Combine AC and DC Ground in a Solar Installation? Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System?
Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System? Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines?
Why are Capacitors Connected in Series in Power Lines?