Basic Voltage, Current, Power and Resistance Formulas in AC and DC Circuits
Following are the electrical engineering formulas and equations for the basic quantities i.e. current, voltage, power, resistance and impedance in both DC and AC circuits (single phase and three phase).
Electrical Current Formulas
Electrical Current Formulas in DC Circuit
- I = V/R
- I = P/V
- I = √P/R
Electrical Current Formulas in Single Phase AC Circuit
- I = P / (V x Cosθ)
- I = (V/Z)
Electrical Current Formulas in Three Phase AC Circuit
- I = P / √3 x V x Cosθ
Voltage or Electrical Potential Formulas
Electrical Potential or Voltage Formula in DC Circuits
- V = I x R
- V = P / I
- V = √ (P x R)
Voltage or Electrical Potential Formulas in Single Phase AC Circuits
- V = P/(I x Cosθ)
- V = I x Z
Voltage Formulas in Three Phase AC Circuits
- VL = √3 VPH or VL = √3 EPH … [Star Connection]
- VL = VPH … [Delta Connection]
Electric Power Formulas
Power Formulas in DC Circuits
- P = V x I
- P = I2 x R
- P = V2/R
Power Formulas in Single Phase AC Circuits
- P = V x I Cosθ
- P = I2 x R Cosθ
- P = (V2/R) Cosθ
Power Formulas in Three Phase AC Circuits
- P = √3 x VL x IL Cosθ
- P = 3 x VP x IP Cosθ
Electrical Resistance Formulas
Electrical Resistance & Impedance Formulas in DC Circuits
- R = V/I
- R = P/I2
- R = V2/P
Electrical Resistance & Impedance Formulas in AC Circuits
In AC Circuits (capacitive or inductive load), Resistance = Impedance i.e., R = Z
- Z2 = R2 + X2 … In case of resistance and reactance
- Z = √(R2 + XL2) … In case of Inductive load
- Z = √(R2 + XC2) … In case of Capacitive load
- Z = √(R2 + (XL– XC)2… In case of both inductive and capacitive loads.
Impedance is the resistance of AC circuits i.e. resistive, captative and inductive circuit (already mentioned above). Where “Z” is the impedance in ohms, “R” is resistance in Ohms and “X” is the reactances in Ohms.
Good to know:
- I = Current in Amperes (A)
- V = Voltage in Volts (V)
- P = Power in Watts (W)
- R = Resistance in Ohm (Ω)
- Z = impedance = Resistance of AC Circuits in Ohms
- Cosθ = Power factor = Phase difference between voltage and current in AC circuits
- VPH = Phase Voltage
- VL = Line Voltage
Also,
XL = Inductive reactance
XL = 2πfL…Where L = Inductance in Henry
And;
XC = Capacitive reactance
XC = 1/2πfC… Where C = Capacitance in Farads.
Also, ω = 2πf
The following table shows the current, voltage, power and resistance equations and formulas in DC and 1-Φ & 3-Φ AC circuits.
| Quantity | DC | Single Phase AC | Three Phase AC |
| Current
(I) |
|
|
|
| Voltage
(V) |
|
|
|
| Power
(P) |
|
|
|
| Resistance
(R) |
|
|
|
Other Additional Electrical Quantities Formulas
Conductance:
G = 1 / R
It is the reciprocal (i.e. inverse) of resistance. The unit of conductance is Siemen or Mho and represented by the symbol of “G” or “℧”.
Capacitance:
C = Q / V
Where “C” is capacitance in farads, “Q” is charge in coulombs, and “V” is voltage in volts. The unit of capacitance is Farad “F” or microfarad “μF”.
Inductance:
VL = -L (di / dt)
Where “L” is inductance in Henrys, “VL” is the instantaneous voltage across the inductor in volts and “di/dt” is the rate of changes in current in Amperes per second. The unit of Inductance “L” is Henrys “H”. It is also known as Ohm’s law for inductance.
Charge:
Q = C x V
Where “Q” is the charge in coulombs, “C” is the capacitance in farads and “V” is the voltage in Volts.
Frequency:
f = 1 / T
Time Period
T = 1 / f
Where “f” is frequency in Hertz (Hz) and “T” is the time periods in seconds.
Related Posts:
- Power Formulas in DC and AC Single-Phase & Three-Phase Circuits
- Electrical & Electronics Engineering Formulas & Equations
- Basic Electrical Quantities Formulas
 Why Do Americans Use Gas Kettles Instead of Electric Kettles?
Why Do Americans Use Gas Kettles Instead of Electric Kettles? Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched?
Why Do The Positive And Negative Wires Spark When Touched? Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Brighter in a Parallel Circuit?
Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Brighter in a Parallel Circuit?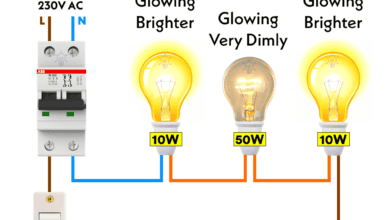 Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Dimmer in a Series Circuit?
Why Does the High-Wattage Bulb Glow Dimmer in a Series Circuit? Difference Between Electronic vs. Electronics Engineering
Difference Between Electronic vs. Electronics Engineering What is Electrical Technology verses Electrical Engineering?
What is Electrical Technology verses Electrical Engineering?