What is RMS Value, Peak Value, Average Value, Instantiations Value, Form Factor, Peak Factor & Other related Terms to AC Circuits and Sine wave?
AC and DC Currents
It is known that the polarity of DC voltage and direction of DC current are always same i.e. it is a unidirectional value which does not change the polarity as well as direction as shown in fig 1.
On the other hand, (AC) Alternating Current or Voltage is one which regularly changes its direction as well as its value. In other words, alternating current (AC) is a type of current which flows first in one direction and secondly, it flows in the opposite direction. In each cycle, it changes the value from zero to the maximum and again hit the zero value.
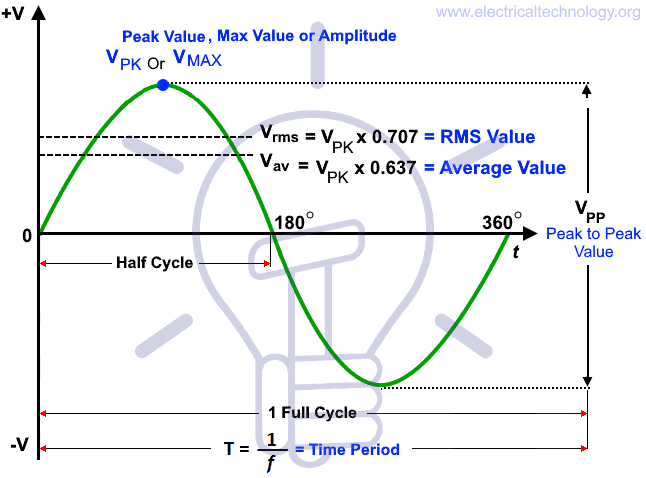
The value of alternating current or voltage can be express in AC (Sinusoidal) Sine wave as shown in fig (1) below.
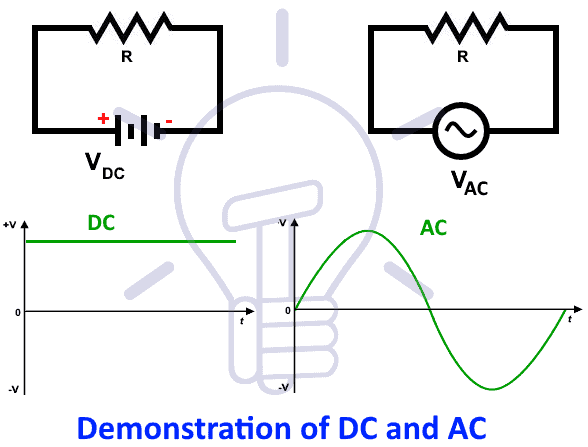
In AC, its not possible to represent the magnitudes as its amplitude of AC sine wave continuously changes with time.
This way, we have multiple options to expressed the magnitude and different values related to an AC sine wave such as:
- RMS Value
- Average Value
- Instantaneous Value
- Maximum or Peak Value
- Peak to Peak Value
- Peak Factor
- Form Factor
- Other related terms
We will discuses all of them in details as follow.
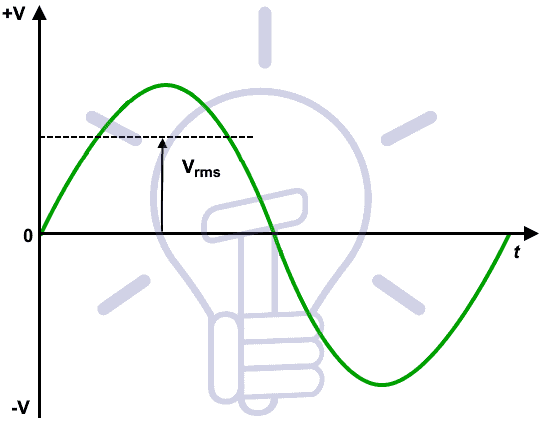
What is RMS (Root Mean Square) Value ?
The RMS (Root Mean Square) value (also known as effective or virtual value) of of an alternating current (AC) is the value of direct current (DC) when flowing through a circuit or resistor for the specific time period and produces same amount of heat which produced by the alternating current (AC) when flowing through the same circuit or resistor for a specific time.
The value of an AC which will produce the same amount of heat while passing through in a heating element (such as resistor) as DC produces through the element is called R.M.S Value.
In short,
The RMS Value of an Alternating Current is that when it compare to the Direct Current, then both AC and DC current produce the same amount of heat when flowing through the same circuit for a specif time period.
or
IRMS = 0.707 x IM , ERMS = 0.707 EM
Actually, the RMS value of a sine wave is the measurement of heating effect of sine wave. For example, When a resistor is connected to across an AC voltage source, it produce specific amount of heat (Fig 2 – a). When the same resistor is connected across the DC voltage source as shown in (fig 2 – b). By adjusting the value of DC voltage to get the same amount of heat generated before in AC voltage source in fig a. It means the RMS value of a sine wave is equal to the DC Voltage source producing the same amount of heat generated by AC Voltage source.

In more clear words, The domestic voltage level in US is 110V, while 220V AC in UK. This voltage level shows the effective value of ( 110V or 220V R.M.S) and it shows that the home wall socket is capable to provide the same amount of average positive power as 110V or 220V DC Voltage.
Keep in mind that the ampere meters and volt meters connected in AC circuits always showing the RMS values (of current and voltage).
For AC sine wave, RMS values of current and voltage are:
IRMS = 0.707 x IM , VRMS = 0.707 VM
To find the RMS value of a sine wave, We may use the following two methods.
- Mid Ordinate Method
- Integration Method.
Lets see how to find the R.M.S values of a sine wave.
Methods for Finding RMS Value of Sine Wave.
Analytical Method
Method 1
We know that the value of sinusoidal alternating current (AC) =
Im Sin ω θ = Im Sin θ
While the mean of square of instantaneous values of current in in half or complete cycle is:
The Square root of this value is:
Hence, the RMS value of the current is (while putting I = Im Sin θ):
Now,
Therefore, We may find that for a symmetrical sinusoidal current:
IRMS = Max Value of Current x 0.707
Method 2.
Let i = Sin ω θ = Im Sin θ
Mean value of i2
Method 3
Let i = Sin ω θ = Im Sin θ
Graphical or Mid-Ordinate Method
This method is known as mid ordinate or graphical method to find the value of RMS voltages by using mid-ordinates or finding the instantaneous value of AC waveform. For clear understanding, a solved example is given below the explanation.
There are many instantaneous voltages in an AC sine wave and its depends on the time interval. As shown in the fig 3 below where the number of mid ordinates are 12, (The more the mid ordinates, the more accurate will be the result). It shows at instance of t = 1, t = 2, t = 3 …. tn, the instantaneous voltages levels are V1, V2, V3 …. Vn respectively.

First, We will find the instantaneous values of voltages for each each time period like t = 1, t =2 … t = n etc. To find the RMS value, We would have to find the square values of each voltage levels in the AC waveform which shows the square part of the RMS Value.
V12 + V22 + V32 + ….. Vn2
Now the squired values of voltages are divided by the number of mid-ordinates which shows the mean value of the RMS voltage.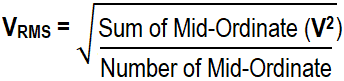
For Example,
Number of ordinates used in above fig 3 = 12
Assume the peak value voltage (Max Voltage i.e. amplitude = VPK or VMax) is 12V for the alternating waveform. The waveform is divided in 12 mid-ordinates as shown below:
| Voltage | 2V | 4V | 6V | 8V | 10V | 12V | 10V | 8V | 6V | 4V | 2V | 0V |
| Angle | 15o | 30o | 45o | 60o | 75o | 90o | 105o | 120o | 135o | 150o | 165o | 180o |
The RMS Voltage is calculated as follow:

This way, The Value of RMS Voltage is 6.97V by using the graphical or mid-ordinate method to find the RMS value of voltage.
- Related Post: Three Phase Current Values in a 3-Phase System
RMS Voltage and Current Equations
RMS Values of Current and Voltage related to Peak Value or Max Value (Both are same).
VRMS = 0.707 x VPK , IRMS = 0.707 x IPK
VRMS = 0.707 x VM , IRMS = 0.707 x IM
RMS Values of Current and Voltage related to Peak to Peak Value.
VRMS = 0.3536 x VP-P , IRMS = 0.3536 x IP-P
RMS Values of Current and Voltage related to Average Value.
VRMS = 1.11 x VAV , IRMS = 1.11 x IAV
Here all in one picture.
RMS Voltage Value Formulas for Different Wave forms
In the below table, the RMS Voltage Value formulas are shown for different kind of sinusoidal wave forms.
| Waveform Type | Formula for RMS Value (VRMS) |
| Sine Wave | VPK / √2 |
| Half wave rectified sine wave | VPK / √2 |
| Full wave rectified sine wave | VPK / √2 |
| Square wave | VPK |
| Triangle waveform | VPK / √3 |
| Sawtooth waveform | VPK / √3 |
RMS Voltage Calculator
In the RMS Voltage Value Calculator, You can calculate the value of RMS voltage from different related values like Average Value, Peak Value and Peak to Peak Value.
What is Average Value
If we convert the alternating current (AC) sine wave into direct current (DC) sine wave through rectifiers, then the converted value to the DC is known as the average value of that alternating current sine wave.

If the maximum value of alternating current is “IMAX“, then the value of converted DC current through rectifier would be “0.637 IM” which is known as average value of the AC Sine wave (IAV).
Average Value of Current = IAV = 0.637 IM
Average Value of Voltage = EAV = 0.637 EM
The Average Value (also known as Mean Value) of an Alternating Current (AC) is expressed by that Direct Current (DC) which transfers across any circuit the same amount of charge as is transferred by that Alternating Current (AC) during the same time.
Keep in mind that the average or mean value of a full sinusoidal wave is “Zero” the value of current in first half (Positive) is equal to the the next half cycle (Negative) in the opposite direction. In other words, There are same amount of current in the positive and negative half cycles which flows in the opposite direction, so the average value for a complete sine wave would be “0”. That’s the reason that’s why we don’t use average value for plating and battery charging. If an AC wave is converted into DC through a rectifier, It can be used for electrochemical works.

In short, The average value of a sine wave taken over a complete cycle is always zero, because the positive values (above the zero crossing) offset or neutralize the negative values (below the zero crossing.)
Related Post: Star Connection (Y): Three Phase Power, Voltage & Current Values
Methods for Finding Average Value of Sine Wave.
Mid-Ordinate or Graphical Method
In this method, the half cycle of a sin wave is divided in equal number of time periods where the duration of each time period is “t/n”.
Suppose the average values of instantaneous currents in each time interval is I2, 12, I3 … In. To find the average value for each time interval, both the left and right vertical lines are added and divided by two. The same apply to all time intervals to find the average value for each instance.
Now, all the average values are added and divided by the number mid-ordinates (i.e. time periods) which shows the overall average of half cycle of a sine wave. the formula for average value is shown below:
Example:
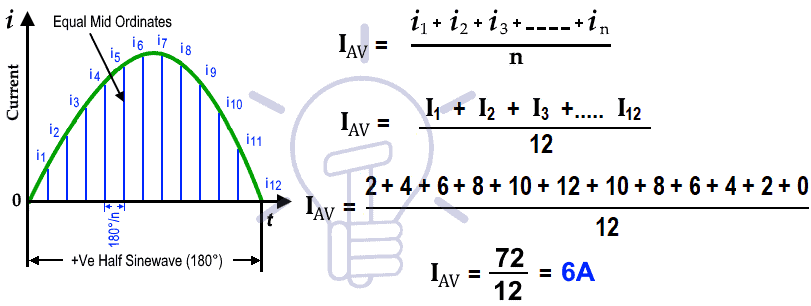
Number of ordinates used in fig 6 = 12
Assume the peak value of current(Max Current i.e. amplitude = IPK or IMax) is 12A for the alternating waveform. The waveform is divided in 12 mid-ordinates as shown below:
| Current | 2A | 4A | 6A | 8A | 10A | 12A | 10A | 8A | 6A | 4A | 2A | 0A |
| Angle | 15o | 30o | 45o | 60o | 75o | 90o | 105o | 120o | 135o | 150o | 165o | 180o |
This way, The Average Value of current is 6A by using the graphical or mid-ordinate method to find the average value of current.
Analytical Method
We know that the standard equation of alternating current is
i = Sin ω θ = Im Sin θ
- Maximum value of current on sine wave = Im
- Average value of current on sine wave = IAV
- Instantaneous value of current on sine wave = i
- The angle specified fir “i” after zero position of current = θ
- Angle of half cycle = π radians
- Angle of full cucle = 2π radians
(a) Average value of complete cycle:
Let i = Sin ω θ = Im Sin θ
Thus, the average value of a sinusoidal wave over a complete cycle is zero.
(b) Average value of current over a half cycle
Average Value of Current (Half Cycle)
IAV = 0.637 VM
Similarly, the average value of voltage over a half cycle
VAV = 0.637 VM
Average Voltage and Current Equations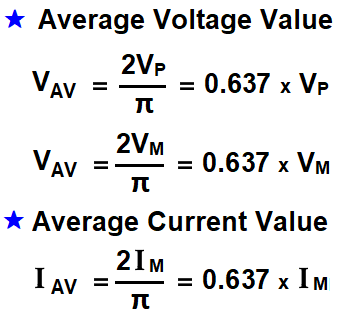
Its mean the value of average voltage or current is equal to multiplication of max or peak value of voltage and current respectively with the constant 0.637.
For example, if the max value or peak value of the sinusoidal wave is 360VPK or 360VMax, by using the above equation, the average value of the voltage would be:
0.637 x 360VPK = 229.32 Av.
Average Value & RMS Value Formulas for Different Wave forms
In the below table, the Average Value and RMS Voltage Value formulas are shown for different kind of sinusoidal wave forms.
| Waveform Type | Formula for RMS Voltage | Formula for Avg Voltage |
| Sine Wave | VRMS = VPK/√2 | VAV = 0 |
| Full rectified wave | VRMS = VPK/√2 | VAV = 0.637 VPK |
| Half rectified wave | VRMS = VPK/2 | VAV = 0.318 VPK |
| Sine wave with DC offset | VRMS = √(VDC2+VPK2/2) | VAV = Vdc |
| Half sine with duration T and frequency f | VRMS = VPK x √(f x T/2) | VAV = 2f x T x VPK/π |
| Positive square wave with duration T and frequency f | VRMS = VPK x √(f x T) | VAV = f x T x VPK |
| Saw tooth wave with duration T and frequency f | VRMS = VPK x √(f x T/3) | VAV = f x T x VPK/2 |
| Trapezoidal wave with frequency f, top segment T, and base segment B. | VRMS = VPK x √(fx ((B-T)+3xT)/3) | VAV = f x VPK x ((T+B)/2) |
What is Instantaneous Value
The value attained by an alternating quantity at any instant is known as instantaneous value. It is denoted by “i” and e.
in other words, the value of an alternating current or voltage at any particular moment us called an instantaneous value.
In fig 7 below, different instantaneous values of voltages or currents are shown at specific point and time period. The value of instantaneous current or voltage are “+” in the positive cycle and “-” in negative cycle in a sinusoidal wave. The curves are showing the values of different instantaneous voltages while the same curve can be drawn for current as well. In the fig 7, the value of instantaneous voltages are 2.5V at 1μs, 5.1V at 2μs, 8.9V at 3μs. While it is -2.3V at 4μs, -6.1V at 5μs and -9.2V at 6μs.

What is Peak Voltage or Maximum Voltage Value ?
Peak value is also known as Maximum Value, Crest Value or Amplitude. It is the maximum value of alternating current or voltage from the “0” position no matter positive or negative half cycle in a sinusoidal wave as shown in fig 8. Its expressed as IM and EM or VP and IM.
Equations of Peak Voltage Value are:
VP = √2 x VRMS = 1.414 VRMS
VP = VP-P/2 = 0.5 VP-P
VP = π/2 x VAV = 1.571 x VAV
In other words, It is the value of voltage or current at the positive or the negative maximum (peaks) with respect to zero. In simple words, it is the instantaneous value with maximum intensity.

Peak to Peak Value
The sum of positive and negative peak values is known as peak to peak value. Its expressed as IPP or VPP.
Equations and formulas for Peak to Peak Voltage are as follow:
VP-P = 2√2 x VRMS = 2.828 x VRMS
VP-P =2 x VP
VP-P = π x VAV = 3.141 x VAV
In other words, the peak to peak value of a sine wave, is the voltage or current from positive peak to the negative peak and its value is double as compared to peak value or maximum value as shown in fig 8 above.
- Related Post: Peak Voltage and Peak to Peak Voltage Calculator
What is Peak Factor
Peak Factor is also known as Crest Factor or Amplitude Factor.
It is the ratio between maximum value and RMS value of an alternating wave.
For a sinusoidal alternating voltage:
For a sinusoidal alternating current:
What is Form Factor
The ratio between RMS value and Average value of an alternating quantity (Current or Voltage) is known as Form Factor.
In the below table, the form factor formulas and values are shown for different kind of sinusoidal wave forms.
| Waveform Type | Formula for Form Factor | Value |
| Sine Wave | π/2√2 | 1.11072073 |
| Half wave rectified sine wave | π/2 | 1.5707963 |
| Full wave rectified sine wave | π/2√2 | 1.11072073 |
| Square wave | 1 | 1 |
| Triangle waveform | 2/√3 | 1.15470054 |
| Saw-tooth waveform | 2/√3 | 1.15470054 |
Other Terms Related To AC Circuits
Waveform
The path traced by a quantity (such as voltage or current) plotted as a function of some variable (such as time, degree, radians, temperature etc.) is called waveform.
Cycle
- One complete set of positive and negative values of alternating quality (such as voltage and current) is known as cycle.
- The portion of a waveform contained in one period of time is called cycle.
- A distance between two same points related to value and direction is known as cycle.
- A cycle is a complete alternation.
Period
The time taken by a alternating quantity (such as current or voltage) to complete one cycle is called its time period “T”.
It is inversely proportional to the Frequency “f” and denoted by “T” where the unit of time period is second.
Mathematically;
T = 1/f
Frequency
Frequency is the number if cycles passed through per second. It is denoted by “f” and has the unit cycle per second i.e. Hz (Herts).
The number of completed cycles in 1 second is called frequency.
It is the number of cycles of alternating quantity per second in hertz.
Frequency is the number of cycles that a sine wave completed in one second or the number of cycles that occurs in one second.
f = 1/T
Amplitude
The maximum value, positive or negative, of an alternating quantity such as voltage or current is known as its amplitude. Its denoted by VP, IP or EMAX and IMAX.
Alternation
One half cycle of a sine wave (Negative or Positive) is known as alternation which span is 180° degree.
Related Posts:
- What is the difference between AC and DC Resistance & How to calculate it?
- How to Find the Number of Nodes, Branches, Loops and Meshes in a Circuit?
- Q Factor in Electrical and Electronics Engineering
- Components of Admittance
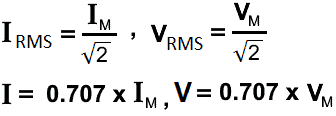

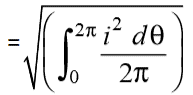
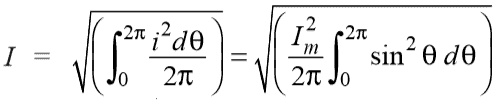
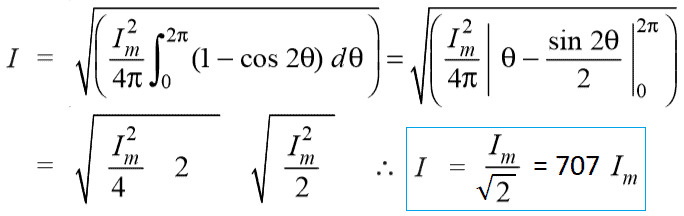

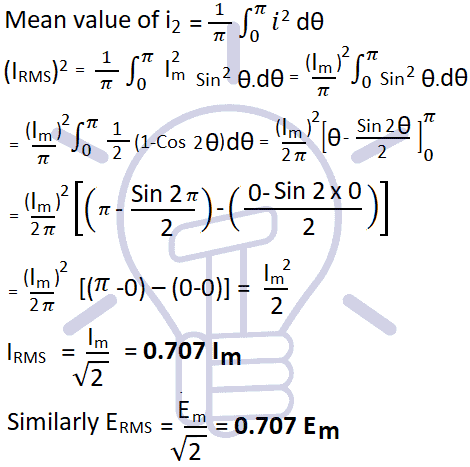
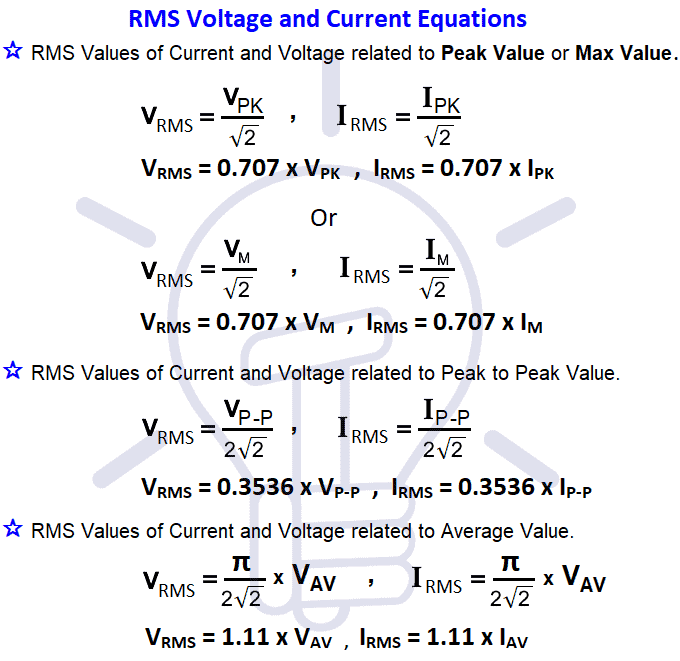

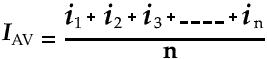
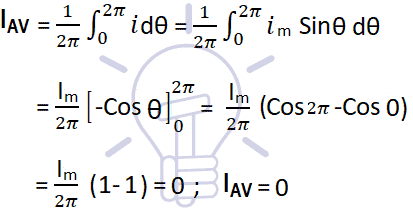
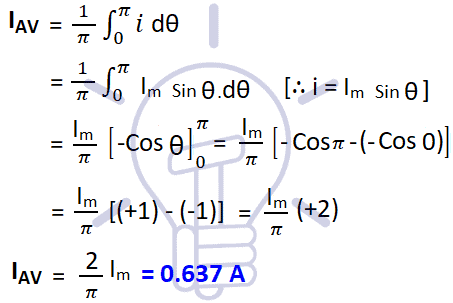

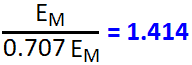
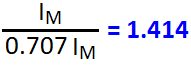
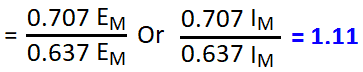
 How to Wire Twin Timer for Repeated ON-Delay in Cycle Mode?
How to Wire Twin Timer for Repeated ON-Delay in Cycle Mode? Wire Twin Timer in Repeat Cycle & One-Shot Mode for 120V/240V Motors?
Wire Twin Timer in Repeat Cycle & One-Shot Mode for 120V/240V Motors? How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay
How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay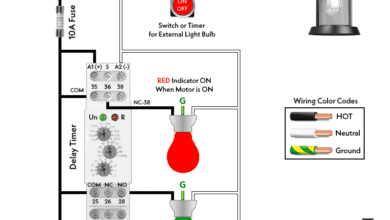 How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?
How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?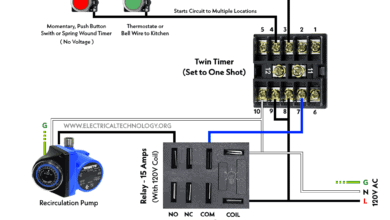 How to Wire One-Shot Timer using Twin Timer For Delay?
How to Wire One-Shot Timer using Twin Timer For Delay? How to Control 120V & 240V Water Heater using ST01 Timer and Contactors?
How to Control 120V & 240V Water Heater using ST01 Timer and Contactors?