Industrial Automation: Types, Hierarchy, and Importance of an Industrial Automation System
Today’s highly competitive industry demands high-quality, consistent products at a competitive price. To meet this challenge, many industries are exploring new product designs and integrated manufacturing techniques, alongside the use of automated devices. One remarkable and influential approach to addressing this challenge is industrial automation.
Industrial automation helps increase product quality, reliability, and production rates, while reducing production and design costs by adopting new, innovative, and integrated technologies and services.
- Related Post: Smart Home Automation System – Circuit and Source Code
What is Industrial Automation?
Automation takes a step further mechanization that uses a particular machinery mechanism aided human operators for performing a task. Mechanization is the manual operation of a task using powered machinery that depends on human decision making.
On the other hand, automation replaces the human involvement with the use of logical programming commands and powerful machineries.
Industrial Automation is the replacement with computers and machines to that of human thinking. The word Automation gives the meaning ‘self dictating’ or ‘a mechanism move by itself’ that derived from the Greek words Auto and Matos where auto means self while Matos means moving.
In a brief, industrial automation can be defined as the use of set technologies and automatic control devices that results the automatic operation and control of industrial processes without significant human intervention and achieving superior performance than manual control. These automation devices include PLCs, PCs, PACs, etc. and technologies include various industrial communication systems.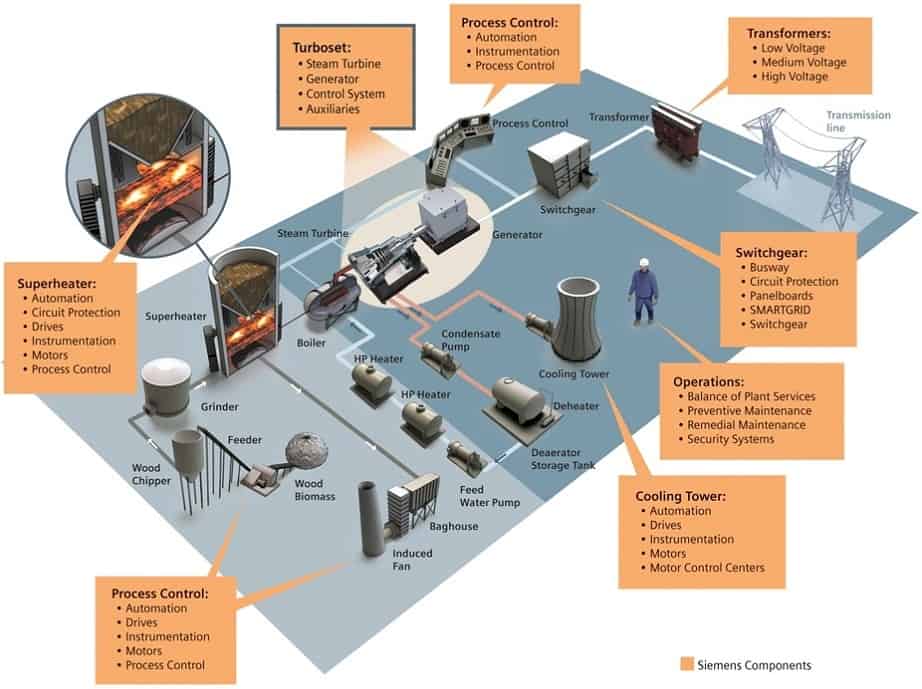
The above figure shows the power plant automation provided by Siemens for achieving sustainable, safe and economic operations. It provides the total integrated automation (TIA) by automating every section of power plant with efficient control devices, field sensors and actuating devices. In this automation, SIMATIC modules (PLCs) are used as control devices while WinCC provides an effective graphical interface.
Related Posts:
- SCADA Systems for Electrical Distribution
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) for Industrial Control
Why is Industrial Automation Important?
- To Increase Productivity
Automation of factory or manufacturing or process plant improves production rate through a better control of production. It helps to produce mass production by drastically reducing assembly time per product with a greater production quality. Therefore, for a given labor input it produces a large amount of output.
- To Provide Optimum Cost of Operation
Integration of various processes in industry with automated machineries, minimizes cycle times and effort and hence the need of human labor gets reduced. Thus the investment on employees has been saved with automation.
- To Improve Product Quality
Since the automation reduces the human involvement, the possibility of human errors also gets eliminated. Uniformity and product quality with a greater conformity can be maintained with automation by adaptively controlling and monitoring the industrial processes in all stages right from inception of a product to an end product.
- To Reduce Routine Checks
Automation completely reduces the need for manual checking of various process parameters. By taking advantage of automation technologies, industrial processes automatically adjusts process variables to set or desired values using closed loop control techniques.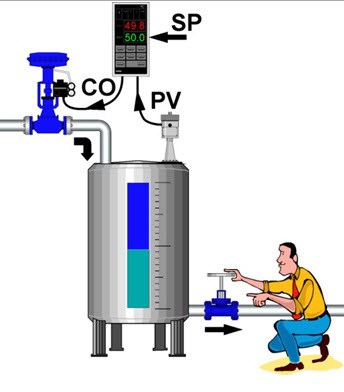
- To Raise the Level of Safety
Industrial automation increases the level of safety to personnel by substituting them with automated machines in hazardous working conditions. Traditionally, industrial robots and robotic devices are implemented in such risky and hazardous places.
Related Post:
- What is AC Drive? Working & Types of Electrical Drives & VFD
- What is DC Drive? Operation and Classification of DC Drives
Hierarchy of an Industrial Automation System
Industrial automation systems can be very complex in nature, having large number of devices working in synchronization with automation technologies. The figure below describes the hierarchical arrangement of the automation system consisting of different hierarchical levels.
Field Level
It is the lowest level of the automation hierarchy which includes the field devices like sensors and actuators. The main task of these field devices is to transfer the data of processes and machines to the next higher level for monitoring and analysis. And also it includes the controlling of process parameter through actuators. For instance, we can describe this level as eyes and arms of a particular process.
Sensors convert the real time parameters like temperature, pressure, flow, level, etc into electrical signals. This sensor data further transferred to the controller so as to monitor and analyze the real time parameters. Some of the sensors include thermocouple, proximity sensors, RTDs, flow meters, etc.
On other hand actuators converts the electrical signals (from the controllers) into mechanical means to control the processes. Flow control valves, solenoid valves, pneumatic actuators, relays, DC motors and servo motors are the examples of actuators.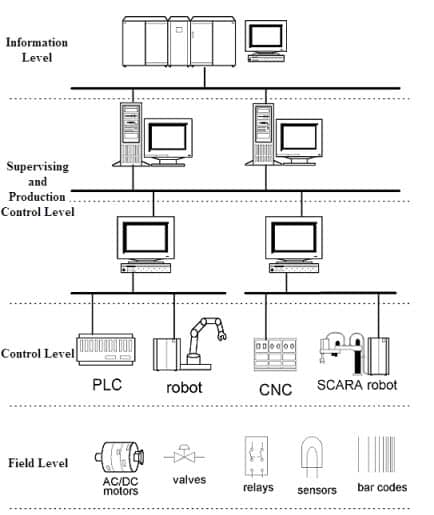
Control Level
This level consists of various automation devices like CNC machines, PLCs, etc., which acquires the process parameters from various sensors. The automatic controllers drive the actuators based on the processed sensor signals and program or control technique.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are most widely used robust industrial controllers which are capable of delivering automatic control functions based on input from sensors. It consists of various modules like CPU, analog I/O, digital I/O and communication modules. It allows the operator to program a control function or strategy to perform certain automatic operation on process.
Supervising and Production Control Level
In this level, automatic devices and monitoring system facilitates the controlling and intervening functions like Human Machine Interface (HMI), supervising various parameters, setting production targets, historical archiving, setting machine start and shutdown, etc.
Mostly, either Distribution Control System (DCS) or Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) HMIs are popularly used in this level.
Information or Enterprise Level
This is the top level of the industrial automation which manages the whole automation system. The tasks of this level include production planning, customer and market analysis, orders and sales, etc. So it deals more with commercial activities and less with technical aspects.
And also industrial communication networks are most prominent in industrial automation systems which transfer the information from one level to the other. So these are present in all the levels of automation system to provide continuous flow of information. This communication network can be different one level to the other. Some of these networks include RS485, CAN, DeviceNet, Foundation Field bus, Profibus, etc.
From the above hierarchy we can conclude that there is continuous information flow from high level to low level and vice-versa. If we assume this graphical way, it is like a pyramid in which as we go up, the information gets aggregated and while going down, we get detailed information about the process.
Related Posts:
- What is a PID Controller? Its Types, Working and Applications
- What are Industrial Communication Networks? An Overview
Types of Industrial Automation Systems
1. Fixed or Hard Automation
This type of automation is employed to perform fixed and repetitive operations in order to achieve high production rates. It uses special purpose or dedicated equipment to automate the fixed sequence assembling or processing operations. Once it is employed, it is relatively hard to change or vary the product design. Therefore, it is inflexible in providing product variety, but increases the efficiency with higher production rate and reduces unit cost.
Some of these automated systems are distilled process, paint shops and conveyors.
2. Programmable Automation
In this automation, a specific class of product changes and also assembling or processing operations can be changed with the modification of control program in the automated equipment.
This automation is best suited for batch production process where product volume is medium to high. But in this, it is hard to change and reconfigure the system for a new product or sequence of operations. Therefore, new product or reconfigure of sequence of operations requires a long setup.
Examples of this automation system are numerically controlled machines, paper mills, steel rolling mills, industrial robots, etc.
3. Flexible or Soft Automation
This automation system provides the automatic control equipment that offers a great flexibility for making changes in the product design. These changes can be performed quickly through the commands given in the form of codes by the human operators.
This automation allows the manufacturers to produce multiple products with different ranges as a combined combination process rather than separate.
Some of the examples of this automation system are automatic guided vehicles, automobiles, and multipurpose CNC machines.
Advantages of Industrial Automation
Industrial automation offers several advantages, including:
- Improved Productivity: Automation can perform tasks faster and more efficiently than human workers, leading to increased productivity.
- Enhanced Safety: By automating dangerous tasks, such as handling hazardous materials or operating heavy machinery, automation can improve workplace safety.
- Higher Quality Products: Automation can reduce errors and variability in production, leading to higher quality products.
- Cost Reduction: While initial setup costs can be high, automation can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced labor costs, improved efficiency, and lower scrap rates.
- Increased Flexibility: Automation systems can often be reprogrammed or reconfigured to adapt to changing production needs, providing greater flexibility in manufacturing.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Automation can streamline the production process, allowing companies to bring products to market more quickly.
- Improved Data Collection and Analysis: Automation systems can collect data on production processes, allowing for better analysis and optimization of operations.
-
Competitive Advantage: Companies that adopt automation early can gain a competitive advantage by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and delivering higher quality products.
Related Posts:
- What Exactly Is A Smart Grid? Smart Grid Applications
- Integration of Renewable Energy with Grid System
- Design & Installation of Control & Monitoring Systems in Electrical Engineering
- Metering, Energy Metering, Monitoring & Measurement Transducers
- Failures In Electrical Systems, Equipment & Materials
- What is Soft Starter? Its Working, Diagram and Applications
- Star Delta Starter – (Y-Δ) Starter Power, Control and Wiring Connection
- STAR-DELTA Starter Motor Starting Method Without Timer
- Direct Online Starter – DOL Starter Wiring Diagram for Motors
- What is Motor Starter? Types of Motor Starters and Motor Starting Methods
- Motor Protection – Types of Faults and Protection Devices
- Types of Electric Motors – Classification of AC, DC & Special Motors
- What is a Contactor ? Types, Working and Applications
- Why Do We Need to Install a Starter with a Motor?
- Single-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Three-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- What is a VFD (Variable Frequency Drive)? – Circuit, Working, Types & Applications



 Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet? Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs?
Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs? How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection?
How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection? How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection
How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables?
How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables? How to Size Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC)?
How to Size Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC)?