HRC Fuse (High Rupturing Capacity Fuse) and its Types
What is High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) Fuse?
A High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) Fuse is a type of fuse used in electrical systems for protection against overcurrent and short circuits. It is designed to safely interrupt high fault currents without causing damage to the surrounding equipment or itself. An HRC fuse can safely handle and interrupt large fault currents, typically up to 80 kA or more, without exploding or creating a fire hazard.
A high rupturing capacity (HRC) fuse contains a fuse wire designed to safely carry short-circuit current for a specified period. During this period, if the fault is cleared, the fuse remains intact; otherwise, it melts and disconnects the circuit from the electrical supply, ensuring the safety of the circuit.
Although glass is a common material used to make HRC fuses, it is not the only option. Other chemical compounds are also utilized in their manufacturing, depending on specific requirements. The external enclosure of an HRC fuse is fully airtight to protect the fuse materials from atmospheric effects. One major concern with HRC fuses is the low and uncertain breaking capacity of semi-enclosed variants.
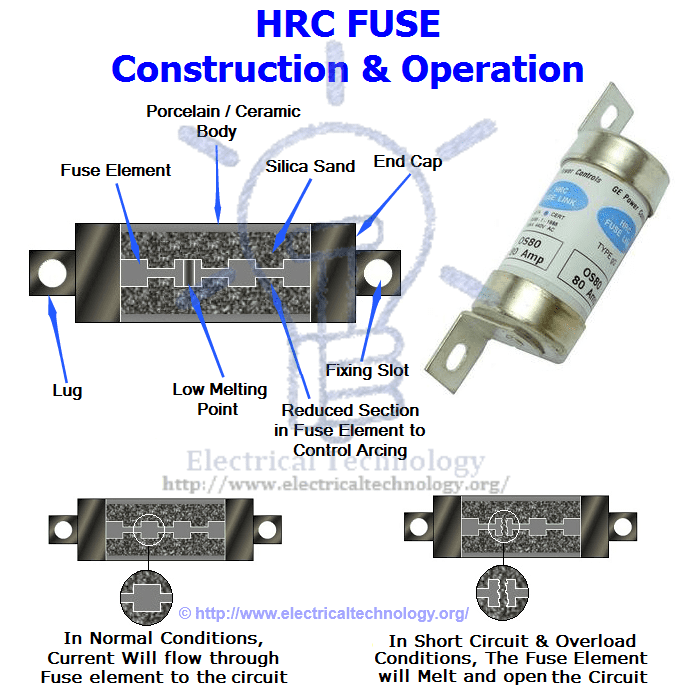
Construction and Operations of HRC Fuse:
An HRC fuse consists of a highly heat-resistant material (such as ceramic) body with metal end caps, which are welded to a silver current-carrying element. The internal space of the fuse body is completely filled with a powder. The material used to fill the inner space may include plaster of Paris, quartz, chalk, marble, dust, and cooling mediums, among others. This filling prevents overheating, allowing the fuse to carry normal current.
The heat produced vaporizes the silver element. A chemical reaction occurs between the silver vapor and the filling powder, resulting in a high-resistance substance. This substance helps quench the arc in the fuse
HRC Fuse with Tripping Device:
When a fuse blows out due to a fault condition, it triggers the tripping device, causing the circuit breaker to operate. The fuse body is made of ceramic material with a metallic cap fixed at each end, connected by a series of silver fuse elements.
At one end, there is a plunger that hits the tripping mechanism of the circuit breaker under fault conditions, prompting it to operate and interrupt the circuit. The plunger is connected through a fusible link and a tungsten wire to the other end of the cap.
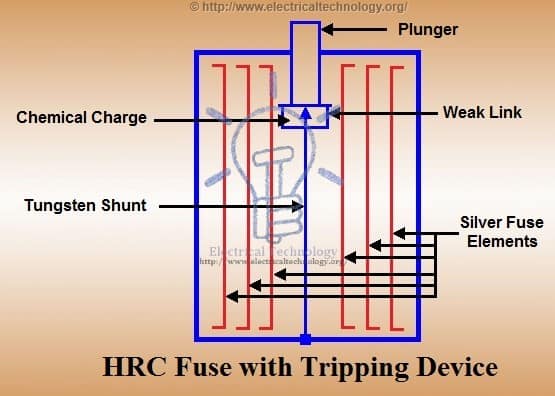
When a fault occurs, the first element to be blown out is the silver fuse, and the current is transferred to the tungsten wire. The travel of the plunger is set in such a way that it is not ejected from the fuse body during fault conditions.
Advantages of HRC Fuse with Tripping Device:
- During a single-phase fault on a three-phase system, the plunger trips the circuit breaker, which opens all three phases, preventing single-phase supply.”
- The effects of the short circuit need to be considered in a circuit breaker to allow the use of an inexpensive circuit breaker.”
- The fuse-tripped breaker is capable of handling small currents, eliminating the necessity of replacing the fuse (except in cases of high current).
Low-voltage H.R.C. fuses are available in capacities ranging from 16,000A to 30,000A at 400V (also available in the range of 80kA to 120kA). HRC fuses are used for protection on low-voltage distribution systems against overload and short-circuit conditions.
- Related Post: Main Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
Types of HRC Fuse:
NH Type
The NH fuse provides overload and short-circuit protection for low and medium voltage. It serves as backup protection for motor starters and other equipment against short circuits and overloads. The fuses are light in weight with compact dimensions.
Din Type
DIN-type fuses are available in a wide range of rated currents. They are used for various purposes, each with specific characteristics under different temperature conditions. These types of fuses are available for different voltage levels and can be utilized in transformer protection even in cases where there is no Low-Voltage (LV) secondary or backup protection. They exhibit excellent clearing capability for ideal low overcurrent with short-circuit performance. DIN fuses also find applications in air and gas-insulated switchgear, mining, transformers, and feeder sectionalizing.
Blade Type
This type of fuse, also known as spade or plug-in fuses, comes with a plastic body and two metal caps to fit into the socket. Mostly used in automobiles for wiring and short-circuit protection, they are lightweight and have a low cutoff current. These fuses are also employed for short-circuit and backup protection of motors. They are available in various sizes and shapes with different current rating capacities, which are printed on the top.
- Related Post: Fuse, Circuit Breaker and Protection Symbols
Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages
- Clears both high and low fault currents.
- Does not deteriorate with age.
- Operates at high speed.
- Provides reliable discrimination.
- Requires no maintenance.
- More cost-effective than other circuit interrupting devices with the same rating.
- Ensures consistent performance.
- Fast fusing operation without noise and smoke.
Disadvantages
- They need to be replaced after each operation.
- The heat produced by the arc may affect the associated switches.
Application of H.R.C Fuses:
- Transformer Protection: H.R.C fuses are commonly used to protect transformers from overcurrent and short-circuit conditions.
- Motor Protection: They are used as backup protection for safeguarding motors against overloads and short circuits.
- Automobiles: H.R.C fuses find application in automotive electrical systems, providing protection for wiring and components.
- Motor Stators: Specifically used in motor stators to ensure proper protection against electrical faults.
- Backup Protection: H.R.C fuses serve as backup protection for various electrical equipment and systems.
- Low Voltage Distribution Systems: These fuses are utilized in low voltage distribution systems to prevent and mitigate the impact of faults.
- Industrial Applications: H.R.C fuses are employed in diverse industrial settings for protecting electrical circuits and equipment.
- Feeder Sectionalizing: They are used in feeder sectionalizing, ensuring the reliability and safety of electrical distribution.
- Air and Gas Insulated Switchgear: H.R.C fuses play a role in protecting components within air and gas-insulated switchgear.
- Mining Operations: These fuses are applied in mining operations for electrical circuit protection.
Final Thoughts
After reviewing the advantages and disadvantages of H.R.C fuses for low-voltage installations, it’s evident that they can be easily replaced. These fuses offer high-speed operation for short-circuit and overcurrent protection. Moreover, they contribute to the stability of industrial power distribution and semiconductor protection. In a low-voltage system, both the fuse and circuit breaker complement each other. They can be used to provide backup protection to the circuit breaker with high breaking capacity.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, RCD (RCCB) and RCBO Circuit Breakers
- Air Circuit Breaker (ACB): Construction, Operation, Types and Uses
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Working, Types & Uses
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
- What is an RCD (Residual Current Device)? – RCB and RCCB
- ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
- What is an RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent)?
- Types of Switches
- Types of Circuit Breakers
- Types of Contactors
- Types of Relays

 Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet? Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs?
Why are there Grooved Slots in the Pins of Two Pin Plugs? How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection?
How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection? How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection
How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables?
How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables? How to Size Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC)?
How to Size Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC)?