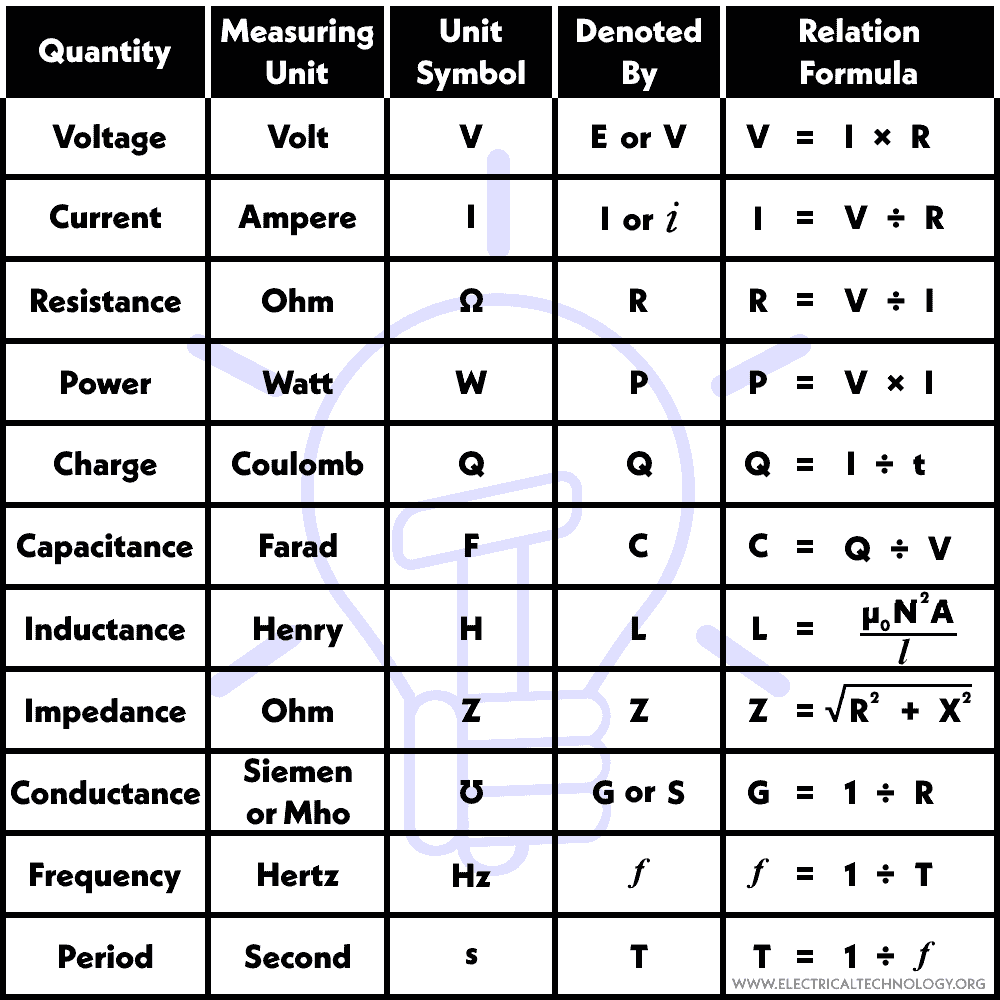
Formulas for Basic Electrical Quantities and Parameter
The following chart provides a list of basic electrical formulas with definitions to calculate and measure basic electrical parameters and quantities. (Formula chart is given below).
Voltage
Voltage is the electric potential difference or electrical force that pushes electric charges through a circuit. Its SI measuring unit is the “Volt” and is denoted by the symbol (V) or (E).
Mathematically,
V = W / Q
Where:
- V = Voltage (in Volts)
- W = Work done (in Joules)
- Q = Electric charge (in Coulombs)
The relation formula of voltage using ohm’s law is follow:
V = I × R
Where:
Electric Current
Electric current is the flow of electric charge (typically electrons) through a conductor. Its SI measuring unit is the “Ampere” and is denoted by the symbol (A).
The relation formula of eclectic current:
I = V ÷ R
Resistance:
Resistance is the opposition that a material offers to the flow of electric current. Its SI measuring unit is the “Ohm” and is denoted by the symbol (Ω).
The relation formula of resistance:
R = V ÷ I
Electric Power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred or consumed. Its SI measuring unit is the “Watt” and is denoted by the symbol (W).
The relation formula of electric power:
P = V × I
Electric Charge
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter, either positive or negative, responsible for current. In other words, the deficiency or excess of electrons in a material is known as electric charge. Its SI measuring unit is the “Coulomb” and is denoted by the symbol (Q).
The representative formula for electric charge:
Q = I × t
Capacitance
Capacitance (C) is the ability of a capacitor to store electric charge. Its SI measuring unit is the “Farad” and is denoted by the symbol (F).
The representative formula for capacitance:
C = Q ÷ V
Inductance
Inductance (L) is the property of an inductor to resist changes in the flow of electric current. Its SI measuring unit is the “Henry” and is denoted by the symbol (H).
The representative formula for inductance:
L = (µ0 N2 A ) ÷ l
Impedance
Impedance (also known as AC Resistance) is the combined opposition of a circuit to the flow of alternating current (AC), encompassing both resistance and reactance. Its measuring unit is the “Ohm” and is denoted by the symbol (Z).
The representative formula for impedance :
Z = √(R2 + X2)
Conductance
Conductance (G) is the measure of a material’s ability to conduct electric current, the reciprocal of resistance. Its SI measuring unit is the “Mho” or “Siemen” and is denoted by the symbol (℧) or (S) respectively.
The representative formula for conductance:
G = 1 ÷ R
Frequency
Frequency (f) is the number of complete cycles or oscillations of a wave or a repeating event (such as alternating current) occurring in a unit of time. Its SI measuring unit is the “Hertz” and is denoted by the symbol (Hz).
The relation formula for frequency:
f = 1 ÷ T
Time period
Time period (T) is the duration it takes for a wave or repeating event to complete one cycle. Its SI measuring unit is the “second” and is denoted by the symbol (s).
The relation formula for time period:
T = 1 ÷ f
Click image to enlarge or open in a new tab
Related Formulas & Equations
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and Equations
- Power Formulas in DC and AC Single-Phase & Three-Phase Circuits
- P, V, I, R, Formulas.( Very Simple)
- Basic/Important Electrical Formulas Library
- Basic Electrical Quantities Formulas in DC Circuits
- Electrical Formulas AC & DC Circuits (Single-φ & 3-φ)
 What is Electrical Engineering? Definition, Branches and Scope
What is Electrical Engineering? Definition, Branches and Scope What is Watt & kW (Watt & Kilowatt)? – Definition, Formula and Calculation
What is Watt & kW (Watt & Kilowatt)? – Definition, Formula and Calculation What is kWh (Kilowatt hour)? – Definition, Formula and Calculation
What is kWh (Kilowatt hour)? – Definition, Formula and Calculation What is Ohm (Ω)? Unit of Electrical Resistance and Impedance
What is Ohm (Ω)? Unit of Electrical Resistance and Impedance Voltage Source: Types of Dependent & Independent Voltage Sources
Voltage Source: Types of Dependent & Independent Voltage Sources Current Source – Types of Dependent & Independent Current Sources
Current Source – Types of Dependent & Independent Current Sources